“Smart grid” is the electric grid that realizes panoramic information operation, 資料傳輸網絡, 動態安全評估, 精細化調度決策, 自動運轉控制, and optimal coordination of the machine and network as well as ensures safety, 可靠性, flexible coordination, high-quality, efficiency, economic-friendly and environmental-friendly.
The article will take you to understand what is a smart grid.
1. 什麼是智慧電網

“Smart grid” typically refers to the new grid system that incorporates modern information systems into the traditional energy network so that the power grid has better control and visibility to cope with difficulties including a low energy utilization rate, poor interactivity, difficult security and stability analysis of the traditional power system. 同時, real-time regulation based on energy flow facilitates the access and utilization of distributed new energy generation and distributed energy storage systems.
A “smart grid” stands for a fully automated power supply network in which every user and node is monitored in real time and the electric current and information are ensured to achieve a two-way flow at every point from the power plant to the customer’s appliances. The smart grid ensures real-time market transactions and seamless connections and real-time interactions among grid members through a wide range of distributed intelligence and broadband communications, as well as the integration of automated control systems.
In the first place, the “smart grid” uses sensors to monitor the operation of key devices in real time such as power generation, 傳染, distribution and supply; Then the system collects and integrates the data obtained through a network system; 最後, the data is analyzed and mined to achieve optimal management of the entire power system.
2. 智慧電網如何運作
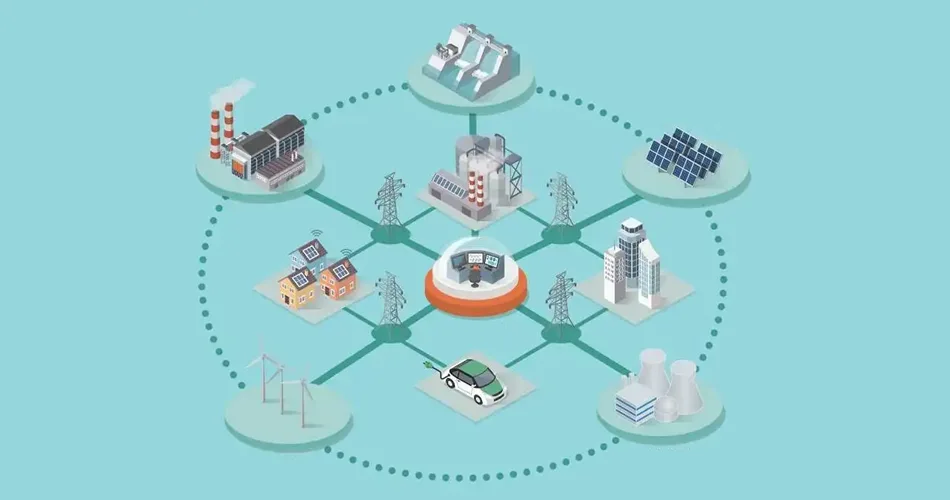
物聯網技術 has a wide application in the power system and can play a significant role in power grid construction, safety production management, operation and maintenance, 安全監控, metering and customer interaction and so on. It can improve the depth and breadth of information perception in all aspects of smart grid generation, 傳染, transformation, distribution and utilization.
發電
In the smart grid power generation and energy storage, IoT technology is mainly applied to the unit operation status detection, electrical parameter monitoring, dam monitoring, station area pollutant and gas monitoring, desulfurization monitoring, energy storage monitoring, in pumped power storage stations. In terms of new energy access like wind farms and photovoltaic power stations, 物聯網 technology applications are reflected in the monitoring of wind power, wind energy, wind speed and wind direction in the distributed field-based station areas. It also conducts the monitoring of light intensity, the number of hours available for light sources and the real-time collection of temperature, 濕度, air pressure, 雨量, 輻射, ice coverage and other elements in the micro-meteorological geographic environments. All of these applications are to achieve automatic monitoring, power prediction and intelligent control of new energy power plants to strengthen the level of coordination of the machine network and optimal allocation of resources so as to ensure the safe and stable economic operation of the energy bases.
電力傳輸
During the process of the smart grid transmission, IoT is applied to ice coverage of transmission line, breeze vibration, shaking, wind deflection, arc sag and tower stress monitoring; By using fiber optic sensing technology, the technology can achieve online monitoring of parameters such as wire temperature, and load capacity dynamic increase as well as early warning; 更重要的是, the technology can achieve monitoring of insulator string wind deflection, fouling and salt density by using passive optical waveguide sensor; By using image or video 感測技術, it can achieve real-time monitoring of anti-theft for line, pylon, tilt, foundation slip, 接地腐蝕為輸電線路故障定位和自動診斷提供技術支撐,為電力線路生產管理和運行維護提供資訊和數位化共享數據, 從而實現安全, 輸電線路高效率智慧巡檢,提升輸電可靠性與安全性.
電力改造
智慧變電站是智慧電網的重要組成部分. 智慧變電站的關鍵在於自動協調控制. 其發展方向是設備資訊和維護狀態數位化,高效能運維是最終目標. 可應用物聯網技術進行即時監控, 用電診斷及輔助決策, mechanization and operation information of substation equipment, especially for oil and gas inspection of transformers using sensing equipment to judge their health status and operation; for protection intrusion detection of substations using wireless sensing, telemetry and three-dimensional virtual technology; IoT realizes protection intrusion detection of substations by using wireless sensing, telemetry and three-dimensional virtual technology; It can also combine electronic identification technology with working ticket system to fulfill smart inspection of substations, operation safety management and scheduling command interactivity in order to boost the growth of unattended digital substations.
配電
A power distribution network is a vital part of an electric power system, having the traits of large amounts of equipment, wide distribution and a complex system. 現在, there are still issues facing China in terms of a weak distribution network frame and difficult communication coverage of the power distribution network. In the strong smart grid distribution process, IoT technology can be applied to achieve automatic power distribution network, power distribution network line and equipment condition monitoring, early warning and maintenance. 更重要的是, it can realize the on-site operation management and intelligent inspection of power distribution network, emergency communication, off-site metering and load monitoring management, distributed energy and charging stations and other facilities monitoring. All of these applications are aimed to strengthen the centralized monitoring of the power distribution network, optimize operation control and management, achieve high-reliability and high-quality power supply and decrease power consumption and losses.
電力利用
Underpinned by a two-way, high-speed and secure data communication network, IoT technology is mainly oriented to smart electricity consumption and interactive technology in the process of smart grid electricity. It is primarily employed for smart electricity service, electricity information collection, smart customer service, electric vehicle charging and electricity replacement, smart business hall, demand-side management and energy efficiency assessment, green environment management of machine rooms and power environment monitoring in order to realize flexible access to the grid, or plug-and-play and two-way interaction with customers to improve electricity supply reliability and electricity consumption efficiency as well as service of power supply enterprises and offer technical backup to national energy-saving and emission reduction strategy.
4. The difference between Traditional Power Grid and Smart Grid 科技

智慧電網五通
In simple terms, a smart grid is the deep integration of advanced information and other technologies into the power grid to achieve fundamental changes in the power industry. It covers all aspects of power generation, 傳染, substation, 分配, consumption and dispatching with the traits of informatization, automation and interaction. Its purpose is to achieve a highly-integrated modern power grid of power flow, information flow and business flow.
Looking back at the traditional power grid, it is not a flexible system, which is reflected in the way that the access and withdrawal of power supply, as well as the transmission of electricity and energy are inflexible, resulting in generating a grid dynamic flexibility and ability to configuration. It is impossible to build a real-time, configurable and reconfigurable system, and there are multiple information silos within the system that lacks the function of information-sharing.
5. 為什麼智慧電網很重要?

智慧電網有什麼好處?
1. In terms of the power system: it can reduce the effective installed capacity of the system, lower the total cost of power generation fuel of the system; enhance the utilization efficiency of the power grid equipment and cut down the construction investment; upgrade the transmission efficiency of the power grid and decrease the line loss.
2. In terms of electricity customers: 實現雙向交互,提供無障礙服務; 提高終端能源利用效率,降低電力消耗; 提高供電可靠性,改善電能品質.
3. 在節能環保方面: 提高能源利用效率,帶來節能減排效益; 推動清潔能源發展,實現替代減排效益; 提高土地資源綜合利用率,減少佔地.
4. 在其他方面: 它可以帶動經濟發展和就業; 保障能源供應安全; 把輸煤改成輸電, 提高能源轉換效率,減輕運輸壓力.
6. 智慧電網面臨的挑戰 系統

The first one is the challenge of a high proportion of new energy grid regulations. 現在, there is increasing pressure on the grid to integrate renewable energy, including the integration of wind power, photovoltaic and customer-side access to distributed power sources, which puts a higher demand on the grid regulation capability.
The second point is the flexible interconnection and safe operation of large grid systems. The State Grid Corporation is currently taking great effort in the construction of ultra-high voltage AC and DC grids, and the flexible interconnection of large grids will become normal for a long time in the future.
The third one is the supply and demand interaction of multiple users of electricity. Lu Yang said that the State Grid Corporation, currently, has established an information collection system for smart grid power consumption, which covers more than 400 million households. 另外, the world’s largest smart car networking platform has been set up with access to more than 170,000 charging stations. 將來, users are engaged deeply in the two-way interaction of the grid, including time-sharing tariffs and demand-side response as well as charging and discharging of electric cars.
The fourth point is the close coupling and interaction between the information space and the power system. Now the big cloud, including advanced information and communication technology, has been more or less utilized in the power grid. The application will be more engaged in the future development trend, with deeper integration into the grid system. 資訊通信技術如何根據業務和應用的需求進行部署將是一個新的挑戰.
7. 智慧電網有哪些設備可供選擇
智慧高壓櫃
與安全雲端計結合, 高壓櫃 (擁有多款無線測溫配套設備) 可實現高壓櫃電量全面監控及平台上傳, 電能體積, 狀態音量和開關電氣接頭, 電纜接頭溫度; 配置為 1 電子身分證並與手機APP結合, 櫃體可實現高壓櫃整體智慧化、雲端化管理
智慧低壓櫃: 單電路
單迴路低壓櫃, 配置1個安全雲表 (外接低壓溫度感測器), can be uploaded directly to the cloud platform to realize integral monitoring and platform uploading of temperature, electrical volume, status volume and electric volume of low-voltage cabinet electrical joints; 配置為 1 電子身分證並與手機APP結合, the cabinet can fulfill the overall intelligence and clouding management of low-voltage cabinets.
智慧低壓櫃: 多電路
Concerning low-voltage cabinets with multi-circuits, each circuit is configured with one electrical safety monitoring instrument (external low-voltage temperature sensors) to centrally upload to the clouding platform, together with another wireless data transmission terminal. 配置為 1 electronic identity card and combined with cell phone APPs, the cabinet can fulfill the overall intelligence and clouding management of low-voltage cabinets with multi-circuits.
智慧箱式變電站
The electrical equipment of the box-type substation contains three parts: high-voltage cabinets, transformers and low-voltage cabinets. 他們之中, safety clouding meters are selected as high-voltage cabinets (equipped with a number of wireless temperature sensors); Inlet and outlet-connected parts of transformers are configured with wireless temperature measurement sensors; Inlet and outlet circuits of low-voltage cabinets are configured with electrical security monitoring instruments (external connection to three temperature-measuring sensors). Through the unified field bus and wireless data transmission equipment connection, it can realize the integral collection and platform uploading of high and low voltage electrical and transformer’s connector temperature, electrical amount, status amount and electricity amount; 配置為 1 electronic identity card and combined with cell phone APPs, the cabinet can fulfill the overall intelligence and clouding management of the overall substations.
智慧電錶
Centralized meter readings and power turn-off can be realized to achieve the turn-on and turn-off of switches through the control of the cell phones.
附除濕裝置的電源櫃
The power cabinet with dehumidification devices provides protection for the power equipment from corrosion.
智慧充電站
Commonly installed in the compounds, such charging stations provide convenience for the residents to charge their electric vehicles outdoors in a smart way.
8. 智慧電網 應用領域

電網數據視覺化
Every detail of the power grid’s operation status can be displayed in a full and complete way to support decision-making and evidence to management, with data analysis including power distribution, 傳染, generation as well as user information, and with visualization operation real-time analysis achieved by software.
電網負載趨勢預測
更重要的是, real-time loading statuses of the Internet can be displayed with the help of historical and real-time data of grid loading provide by big data, which can predict the changing trend of grid loading. 也, along with comprehensive management, it can boost the utilization rate of devices and decrease power consumption and losses to achieve a more economical and efficient power grid operation.
設備故障趨勢預測
By analyzing the correlation among fault types, historical status and operational parameters of faulty equipment in the grid analysis through big data, the pattern of grid fault occurrence can be predicted. 也, the risk of grid operation can be assessed. All of these can give real-time early warning, allowing technicians to conduct equipment maintenance and inspection ahead of time.
網格自修復實現
In a smart grid, faulty devices in the grid are isolated from the grid system as quickly as possible, and the system restores itself to normal operations (with little or no human intervention), thus providing virtually uninterrupted power service to customers. We can draw an analogy that the human immune system is similar to the self-healing of the smart grid. Combining the two predictions above, the grid system can continuously achieve self-predicting and take instant measures to control or correct faults which have been detected or are likely to occur.
二次設備獨立通信
Within existing grid systems, communications of secondary devices are usually achieved through buses and special communication devices, which are called “master control units” (generally called RTUs) in internal terms. In a smart grid, secondary devices such as monitoring and protection will be equipped with self-adaptive as well as self-interactive modules that can communicate with each other adaptively. This flexibility and self-adaptive capability will significantly enhance reliability as if the equipment were “autonomous”. 在這種情況下, other devices can still be in stable operation even if parts of the system function in failure.
















