Internet of Things mangrupikeun salah sahiji téknologi anu pang populerna dina révolusi téknologi ayeuna tapi masih nyanghareupan seueur tantangan IoT.. Nalika alat sareng téknologi janten nyambung sareng langkung pinter, kitu ogé bahaya sarta vulnerabilities aranjeunna nyanghareupan. Dina dékade kaliwat, éta Internét tina hal geus loba dipaké dina sagala rupa industri, kalawan loba pausahaan ngagunakeun eta pikeun ngembangkeun operasi smarter.
Sedengkeun alat IoT mawa komunikasi efisien antara alat, otomatis, ngahemat waktos sareng biaya, sarta loba mangpaat séjén, aya ogé hiji hal ngeunaan pamaké, sareng éta sanés kaamanan. Alat IoT hésé dipercaya dina sababaraha waktos. Tulisan ieu bakal ngagoda sababaraha tantangan IoT konci dina unggal tautan.
1. 8 Tantangan IoT dina Masalah Kaamanan

Standar kaamanan non-konsisten
Internet of Things rada katinggaleun dina hal standar kaamanan. Henteu aya standar anu seragam pikeun pasar sareng usaha niche, anu hartosna yén sadaya usaha diwajibkeun nyetél pedoman sareng protokol sorangan.
Kurangna standarisasi ngajantenkeun langkung hese pikeun ngamankeun Internét tina hal-hal sareng komunikasi antara M2M tanpa ningkatkeun résiko.
kapasitas processing low
Aya saeutik pisan data anu diperlukeun pikeun kalolobaan aplikasi IoT. Ieu manjangkeun umur batre sareng ngirangan biaya, tapi ngajadikeun apdet OTA leuwih hese tur prohibits alat ngagunakeun parabot kaamanan jaringan. Ku kituna, Hacking condong lumangsung.
Aset warisan
Ngembangkeun aplikasi tanpa konektipitas awan rentan ka serangan cyber modern. Salaku conto, aset heubeul ieu bisa jadi teu sasuai jeung standar enkripsi anyar. Ieu bahaya mun ngantep aplikasi heubeul dijalankeun dina Internet tanpa nyieun parobahan badag, tapi éta teu salawasna mungkin kalawan aset bersejarah. Téknologi ieu parantos dihijikeun - sigana mangtaun-taun - komo apdet kaamanan leutik mangrupikeun tantangan IoT utama..
Kurangna kasadaran
Pamaké Internét parantos diajar kumaha ngajagi telepon sélulér sareng komputer pribadi salami mangtaun-taun. Tapi kusabab Internet of Things mangrupakeun téhnologi anyar, loba jalma anu teu wawuh jeung konsep jeung fungsi na. Lantaran kitu, konsumén, usaha sareng pabrik tiasa nyababkeun ancaman kaamanan pikeun alat-alat Internét. Peretas nyerang jalma sareng alat.
Serangan botnet
Botnets mangrupakeun jaringan alat numbu nu nyumputkeun malware, ngamungkinkeun para pembajak pikeun ngalakukeun sagala jinis panipuan. Bot sapertos kitu diadopsi pikeun ngalaksanakeun kacilakaan server, aksés teu sah, panolakan disebarkeun jasa, jeung maling data.
Tujuan biasa nyaéta pikeun ngembangkeun, ngajadikeun otomatis, sareng ngagancangkeun serangan dina waktos anu pondok sareng ngirangan biaya. Pikeun nyerang sacara efektif, hacker a bisa jarak jauh ngakses alat jeung nginféksi rébuan workstations. Hésé pikeun sistem anu aman pikeun ngabédakeun komunikasi anu nyata sareng anu jahat.
Kurangna énkripsi
Dina Internét tina Hirup, kurangna enkripsi transmisi tradisional mangrupa salah sahiji masalah kaamanan pangbadagna. Aranjeunna tiasa nampi inpormasi sénsitip anu dikirim ka sareng ti alat nalika aya anu ngarecah kana jaringan.
Apdet firmware leungit
Isu gedé anu sanés pikeun kaamanan IoT nyaéta naha alat anu disebarkeun rentan. Pabrikan kedah ningkatkeun firmware na naha éta asalna tina kode sorangan atanapi kode anu dihasilkeun ku pihak katilu. Dina tiori, ieu kedah tiasa jarak jauh, tapi ieu teu salawasna mungkin. Lamun data pindah lalaunan teuing sakuliah jaringan atawa kapasitas pesen diwatesan, Anjeun bisa jadi kudu ngahubungan fisik alat pikeun ngaleupaskeun apdet.
Alat Internet of Things anu dilarang sareng palsu
Nutup wates sareng ngatur sadaya alat individu mangrupikeun tantangan utama kaamanan IoT. Popularitas alat Internét sareng paningkatan gancang dina jumlah alat anu diproduksi parantos nyababkeun masalah sareng jaringan asal.
Pangguna anu henteu sah masang alat IoT anu ilegal sareng palsu dina jaringan anu ditangtayungan.
Alat sapertos kitu tiasa dikonpigurasikeun salaku titik aksés jahat, thermostats, jeung kaméra pikeun maok data komunikasi tanpa pangaweruh pamaké.
2. Internét tina hal(IoT) tantangan dina Privasi Data

Privasi mangrupikeun perhatian utama pikeun usaha. Isu kumaha cara ngajagaan data sénsitip sareng pribadi langkung saé janten langkung menonjol dina taun-taun ayeuna, salaku kerangka hukum sareng pangaturan sapertos GDPR parantos nampi perhatian anu langkung ageung sareng bentang ancaman cyber janten langkung dinamis sareng kompleks..
IoT ngarobih sababaraha industri, sareng automation sareng intelegensi bisnis anu digampangkeun éta kuat. Tapi IoT ogé nampilkeun tantangan khusus pikeun organisasi dina hal privasi data. Hayu urang diajar tina eusi di handap ieu.
Ngaronjat titik tungtung
sénsor IoT atawa alat disambungkeun ka Wéb. Ieu, dina waktosna, hartina alat atawa sensor IoT mangrupakeun titik poténsi leakage data, atawa pihak jahat bisa meunang aksés.
Ku kituna, nalika hiji organisasi nyiptakeun ékosistem IoT, salaku conto, ku deploying sensor networked sakuliah sakabéh aset fisik lantai pabrik, masing-masing aset fisik éta sacara téoritis mangrupikeun alat tungtung, sapertos komputer sareng alat sélulér di tempat sanés dina organisasi. Salaku hasilna, grup geus greatly ngaronjat beungeut serangan, nu cybercriminals bisa nyoba mangtaun aksés ka jaringan ngaliwatan alat terminal guna maok data.
Alat leutik tur basajan
Henteu ngan ukur jumlah alat IoT anu nyababkeun masalah privasi, tapi kesederhanaan jeung ukuran leutik loba di antarana. Ieu biasana hartosna teu mungkin pikeun nampilkeun panyalindungan kaamanan jaringan canggih dina alat ieu, hasilna inféksi malware jeung interception data jahat. Masalah sanésna tiasa kalebet netepkeun kecap konci anu gampang diinget kana kecap konci standar.
nambahan data
Alat IoT ngumpulkeun data anu mustahil pikeun ngumpulkeun atanapi mahal. Data ieu ngahasilkeun sajumlah ageung intelijen bisnis anu tiasa dianggo sacara real-time sareng jangka panjang. Pondokna, aranjeunna nyirorot ngaronjatkeun jumlah organisasi data anu nanganan - nu, dina waktosna, hartosna yén ahli kaamanan sareng privasi kedah merhatikeun kumaha data éta dikumpulkeun, diolah, dibagikeun, sarta disimpen.
Pikeun nerapkeun pendekatan anu kuat pikeun panyalindungan privasi data, organisasi anu ngolah data, utamana data pribadi, kudu peta yén aliran data sakuliah bisnis maranéhanana sarta draf na enact kawijakan kaamanan patali data éta.
Visibilitas mangrupakeun konci
Masalah privasi sareng panyalindungan data ieu sigana tiasa seueur rupa, tapi aranjeunna henteu insurmountable. Gantina, perusahaan anu kalibet dina ngembangkeun atanapi nyebarkeun alat IoT kedah ngajantenkeun panyalindungan data janten prioritas ti mimiti, lain tambihan pikeun tinimbangan engké. Privasi data anu kuat salawasna dimimitian ku pisibilitas - ngartos naon data anu dikumpulkeun atanapi dibangkitkeun, dimana jeung kumaha eta diolah, jeung kumaha eta keur disimpen.
3. IoT Tantangan di Konektipitas Komunikasi Nirkabel
Sedengkeun wengkuan pinuh ku Internet of Things masih keur didebat, Éta écés yén alat-alat ieu aya dina persimpangan jalan nalika aranjeunna ngalih tina "saé pikeun gaduh" kana "penting.,” and people will increasingly rely on these devices to perform mission-critical and, sometimes, critically important applications.
Wireless communication is crucial for Internet of Things alat. ZigBee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth, NB-IoT, and Wi-Fi are preferable options for designers to enable this communication. Internet of thing devices must operate across multiple users with different wireless technologies and the same spectrum in mission-critical scenarios.
In large buildings (such as hospitals), intensive equipment operations must be provided and reliable wireless communications must be carried out. Patient tracking devices, cahaya pinter, alat wearable, medical devices, and security systems carried by visitors must operate simultaneously and not interfere with each other. This situation exists in hospitals, where medical surveillance equipment shares the 2.4 GHz ISM band with mobile phones, wireless cameras, and microwave ovens. Penting pikeun mastikeun yén operasi alat IoT tiasa dianggo sakumaha anu dimaksud dina lingkungan jinis ieu.
tantangan jaringan
Kalayan mecenghulna 5G, beuki loba aplikasi bakal ngagunakeun ningkat kinerja jaringan sélulér pikeun "ngalirkeun" workload komputasi ka puseur data.. Alat tina sagala jinis tiasa dihubungkeun ka jaringan, sababaraha diantarana tiasa ngahaja ngabahayakeun kaamanan sareng integritas jaringan. Ku kituna, sistem sareng alat manajemén jaringan kedah dikembangkeun pikeun ngirangan résiko sapertos kitu.
Kamampuan IoT ayeuna dirarancang pikeun dianggo dina aplikasi anu beuki kritis dina sadaya séktor industri. Désainer kedah nuturkeun prosés anu dipikiran saé pikeun ngarancang, nguji, sareng ngesahkeun alat sareng sistem pinterna. Prosésna kedah ngalibetkeun pangukuran sareng uji dina komunikasi nirkabel, tingkat jaringan, jeung alat.
Kabeneran, Désainer ayeuna gaduh sababaraha pilihan tés anu sayogi pikeun ngabantosan pungsionalitas ékosistem IoT. Tapi ngalakukeun tés anu leres henteu cekap. Désainer kedah ngadopsi alat anu leres pikeun ngalakukeun padamelan anu leres.
Analisis konsumsi batré mantuan désainer akurat nangtukeun pamakean alat ayeuna jeung lilana unggal mode operasi. Alat modél anu akurat sareng simulasi EMI tiasa ngabantosan estimasi tingkat émisi sateuacan pangwangunan hardware.
4. Biasa Pangwangunan IoT Tantangan
Modul sensor
Modul sénsor biasana dirarancang sakitar unit mikrokontroler anu gaduh antarmuka digital sareng analog, sarta panganteur RF transceiver ogé diperlukeun pikeun komunikasi jeung dunya luar.
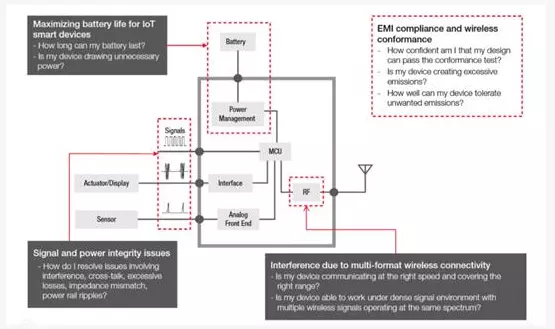
Diagram blok hiji modul sensor IoT
Manajemén kakuatan sareng ukuran mangrupikeun tantangan umum pikeun désainer. RF interfaces can consume a lot of power. Low-power wireless protocols have been developed to offer a trade-off between power consumption and transmission range. Power consumption and smart factories in some environments may not be an issue compared to the requirement that multiple devices must communicate without interference. Signal integrity becomes an essential priority. Salaku tambahan, electromagnetic interference requirements must be complied with in industrial environments.
Designing IoT devices with optimal battery life requires accurate power consumption curves and accurate characterization of the dynamic load on the device. Understanding the relationship between load requirements, and time required is an essential aspect of determining possible battery life.
Naha éta téh batré tombol non-rechargeable atawa batré LiPo rechargeable, Karakteristik operasi batré kedah dipikahartos sareng dilebetkeun kana program manajemén kakuatan anu kompleks pikeun manjangkeun sareng ngaoptimalkeun umur batre.. Bisa ngalacak beban batré sareng kumaha syarat tiasa ngabantosan.
Désainer tiasa ngembangkeun prosés manajemén kakuatan anu kuat ku ngagunakeun inpormasi ieu. Désainer bisa nangtukeun, salaku conto, yén ayeuna tina alat IoT boga rentang dinamis pisan lega salila operasi, tina ratusan milliamps nalika transceiver nirkabel ngamimitian link ka submicroamps nalika transceiver pareum, nepi ka mikrokontroler nyaeta maksimum. Pola saré optimal, sensor teu diaktipkeun, teras salajengna.
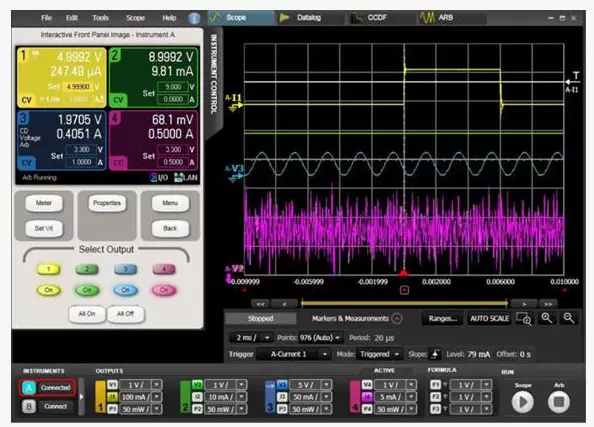
Angka 2. Penting pikeun ngaoptimalkeun umur batre pikeun nganalisis konsumsi batré dina alat IoT nirkabel. Analis kakuatan N6705B DC sareng N6781A dua unit pangukuran sumber kuadran mangrupikeun alat anu idéal pikeun ngémutan konsumsi batré sareng ngartos parobihan alat dina waktosna sareng beban batré..
umur batre panjang
Seueur pangguna alat IoT ayeuna ngabutuhkeun yén aranjeunna gaduh batré anu tahan mangtaun-taun. Ieu hususna penting upami aya anu ngarencanakeun nyebarkeun hiji hal di daérah anu terpencil dimana aranjeunna henteu gampang ngaksés batré anu robih. Operasi atawa lamun heunteu nempatkeun batur dina resiko luhur komplikasi bisa jadi diperlukeun ku sering ngaganti batré.
Désainer hardware kedah mikir ngeunaan aspék mana anu bakal ngonsumsi kakuatan anu paling ageung sareng naha éta kedah dilebetkeun kana desain.
Using integrated circuits that have deep sleep patterns and consume very little current can solve this challenge. Sumawona, designers should also take consideration into how to use low battery voltages. Salaku conto, minimize the current consumption of the product. Designers can achieve this by using low-power components and ensuring that parts do not continue to consume too much power when not in use.
Researchers who have commented on the project believe significant progress will be made by developing batteries that can charge themselves.
vulnerabilities kaamanan
Current headlines often contain alarming details about security vulnerabilities that could affect IoT devices around the world. A multi-pronged approach is required to solve this internet of things design challenge from a hardware perspective.
Anu mimiti, designers must consider secure key management. Ngagunakeun enkripsi hardware-gancangan pikeun ngajaga alat leuwih aman oge hiji pilihan.
domain memori misah oge metoda pikaresep. Anggo aksés mémori anu aman pikeun ngajaga mémori lampu kilat sareng RAM tina aksés anu henteu sah. Lakukeun kitu ngajadikeun leuwih hésé pikeun hacker pikeun ngajalankeun serangan ngagunakeun interfaces programming jeung debuggers.
Nyorong pikeun torek, alat nu leuwih leutik
Kahayang pikeun fitur ieu diyakinkeun sabab ngamungkinkeun kalenturan dina palaksanaan.
Hiji kamungkinan nyaéta ningali naha alat kedah nganggo papan sirkuit dicitak anu fleksibel (PCBs) tinimbang kaku. Langkung komponén diidinan pikeun dipak kana rohangan anu langkung alit. Éta ogé umumna langkung awét tibatan anu kaku sareng tiasa langkung tahan guncangan dina lingkungan anu parah, masihan aranjeunna umur panjang sadayana.
Lamun alat IoT bakal dipaké ditéang jeung kacerdasan buatan (AI) atawa ngolah data dina alat, hardware designers must understand that these necessities also affect form factor dimensions.
IoT hardware designers should keep up with these developments and understand how newer options support their upcoming products.
Investasi cukup waktu dina nguji
Designers usually operate on a tight schedule. Even so, they must allow enough time to test the hardware and make the necessary adjustments once the results are in.
Testing before a product is marketed can also prevent safety-related problems. Salaku conto, fuzzy testing involves getting IoT devices to accept random bytes and track abnormal behavior that might indicate an error. This most often happens when testing a computer application. Tapi, it’s also a good method to check the internet of things devices.
Effective communication across teams is critical to obtaining useful test results. Pamekar parangkat lunak anu dianggo dina alat tiasa mendakan kasalahan anu sawaréh mangaruhan hardware.
Ngadegkeun hubungan anu stabil sareng panguji ogé penting. Seueur pihak ieu panginten henteu langsung terang yén aranjeunna ngalaman masalah kusabab masalah hardware. Sanajan kitu, sanggeus eupan balik lengkep ti maranéhanana kalibet dina nguji, Désainer hardware sareng anu sanésna aub dina produk IoT tiasa mimiti terang dimana masalahna sareng kolaborasi pikeun ngalereskeunana.
Désainer hardware kedah salawasna ngarencanakeun pikeun nyéépkeun waktos langkung seueur tés ti anu disangka. Jalan dieu, euweuh tekanan pikeun rurusuhan hal, tur euweuh kasempetan leungit masalah anu bisa ngaganggu fungsionalitas produk atawa kaamanan engké on.
Foresight nyegah seueur tantangan desain IoT
Henteu aya hiji-ukuran-cocok-sadaya cara pikeun nyingkahan unggal tantangan desain IoT. But it is critical to consider the good and bad consequences of each design decision. Designers can also be able to make the most suitable options at each stage and avoid time-consuming problems.
5. IoT Challenges in Deployment

IoT deployment has expanded from consumer-based applications like imah pinter devices and wearables to mission-critical applications in industrial automation, tanggap darurat, kaamanan umum, IoMT, and autonomous vehicles.
The “5C” for the IoT are the 5 primary challenges facing IoT design, namely continuity, konektipitas, compliance, kaamanan jaringan, and co-existence.
tangtangan deployment 1: Konektipitas
Achieving a seamless flow of information to and from devices, infrastruktur, awan, and applications is one of the larger IoT challenges because of the complexity of intensive device deployments and the complexity of wireless connectivity. Sanajan kitu, mission-critical IoT devices are expected to function reliably without failure even in the harshest environments.
Solutions are required to be designed and tested that are highly configurable, fléksibel, and scalable to meet future requirements to address connectivity challenges. Flexibility needs to test devices with multiple radio formats in actual operating mode and to support OTA testing in signaling mode without chipset-specific drivers. To leverage the code and minimize measure-related issues at different stages of development, the solution should be inexpensive, basajan, and able to be used in manufacturing and R&D.
tangtangan deployment 2: Kasaluyuan
Ensuring and extending battery life is essential. Longer battery life is a big benefit. For IIoT devices, battery life is typically 5~10 years. Hirup alat hartosna bédana antara maot sareng kahirupan pikeun alat médis. Sanajan kitu, cacad batré oge masalah.
Désainer IC diwajibkeun mendesain ics kalayan mode sare jero sareng ngirangan instruksi sareng set kagancangan sareng ngahontal voltase batré rendah pikeun nyumponan sarat umur batre IoT., sirkuit terpadu.
Badan standar ngahartikeun modeu operasi kakuatan rendah sapertos Sigfox, LTE-M, LoRa, jeung NB-IoT, nu ngajaga konsumsi kakuatan low bari nyadiakeun waktos operasi éféktif kawates.
tangtangan deployment 3: minuhan
Alat Internet of things dibutuhkeun pikeun sasuai sareng sarat pangaturan global sareng standar radio. Uji konformasi kalebet pamariksaan standar radio sareng uji katampi pamawa, ogé tés patuh pangaturan, sapertos RF, EMC, jeung tés SAR. Design engineers are usually forced to adhere to strict product launch schedules in compliance with the latest regulations
As compliance testing is time-consuming and complex, days or weeks are required to complete if performed manually. In order to keep the release schedule, designers can consider investing in in-house pre-conformance testing solutions that can be used at every design stage, as well as resolving problems early. Selecting a system that meets the regulatory compliance requirements of the test lab can also help ensure measurement relevance and reduce the risk of failure.
tangtangan deployment 4: Hirup babarengan
For billions of devices, congestion in radio channels is a problem that is only going to get worse. Badan standar parantos ngembangkeun tés pikeun meunteun kumaha alat beroperasi dina ayana sinyal sanés pikeun ngabéréskeun kamacetan nirkabel.
Salaku conto, dina Bluetooth, frékuénsi adaptif hopping (AFH) ngamungkinkeun alat Bluetooth ngantunkeun saluran anu ngalaman tabrakan data anu luhur. Téknologi pencegahan tabrakan anu sanés, sapertos LBT sareng CCA, ogé bisa ningkatkeun efisiensi transmisi. Tapi efektivitas dina lingkungan sinyal campuran teu jelas, jeung lamun format radio teu bisa ngadeteksi silih, konflik jeung leungitna data bisa lumangsung.
Sensor industri anu kaleungitan kadali sinyalna tiasa gaduh akibat anu serius. Coexistence testing is therefore essential to measure and evaluate the operation in crowded mixed-signal environments and to assess the potential risks of maintaining wireless performance when unexpected signals are found in the same operating environment.
tangtangan deployment 5: Kaamanan jaringan
Most traditional network security tools are focused on the web and the cloud. OTA and Endpoint vulnerabilities are often overlooked. Little work has been done to address OTA vulnerabilities through mature technologies such as WLAN and Bluetooth used in many applications.
70% of security vulnerabilities come from endpoints. To protect these IoT devices, extra care should be taken. Potential entry and OTA vulnerabilities points into endpoint devices should be identified, and devices should be tested with a regularly updated database of known threats/attacks.
Bangun yayasan Internét anu solid ngaliwatan "5C"
Éta muka panto pikeun kasempetan anyar anu pikaresepeun sareng aplikasi pikeun seueur industri. Tapi ogé nampilkeun tantangan anu teu pernah aya, merlukeun cara anyar pamikiran pikeun minuhan sarat misi-kritis. Ngirimkeun IoT anu suksés hartosna ngatasi tantangan téknologi 5C IoT. IoT ngalaksanakeun janjina sareng bakal dipastikeun ku ngagunakeun validasi anu leres, nguji minuhan, manufaktur, sareng alat kaamanan sapanjang siklus kahirupan produk.
6. Tantangan ranté suplai industri IoT

Tinjauan dasar tina Internet konsumen of Things
IoT ngarujuk kana ngahubungkeun objék naon waé ka jaringan poténsial saluyu sareng protokol pangiriman khusus sareng ngawujudkeun sambungan anu cerdas antara hal-hal., hal, jalma, jeung jalma ngaliwatan transmisi real-time jeung kumpulan informasi multi-dimensi. Salaku wawakil revolusi katilu dina industri téhnologi informasi, the IoT organically combines AI computing AND traditional industrial manufacturing. The IoT is primarily divided into Industrial Internet of Things and consumer IoT.
The complete IoT is mainly composed of the network layer, lapisan aplikasi, perception layer, and platform layer. As the integrator of the Internet of Things, the application layer undertakes the important responsibility of realizing product functions for end-users. The company’s main product, intelligent audiovisual hardware, belongs to the application layer of the consumer Internet of Things. Consumer IoT, smart office, smart travel, and smart home are In the application scenarios of consumer IoT.
Data mangrupikeun sumber daya inti jaman IoT
Intelligent terminal is the entrance to the Internet of Things to obtain data: Jalur évolusi ti jaman Internet ka jaman Internet of Things umumna diringkeskeun kieu: Internét (PC, 1.0 jaman) → Internét mobile (telepon pinter, 2.0 jaman) → Internét of Things (terminal calakan interaksi manusa-komputer jeung Internet sagalana, 3.0 jaman), sarta unggal pamutahiran ieu dipuseurkeun kana pertambangan jeung redistribution data lalulintas, sumberdaya inti. Internet of Things bakal megatkeun ngaliwatan sambungan "jalma" aya, ngalegaan ka "jalma", "jalma jeung hal", "Hal-hal sareng hal-hal" "Internet sadayana", sareng dina dasar ieu ngahasilkeun data anu langkung ageung, AI leuwih kuat. Sumber daya inti jaman Internet of Things nyaéta data. Naha éta chip, sénsor, terminal calakan sarta pabrik hardware séjén, atawa operator komunikasi, platform awan, intelijen buatan sareng perusahaan jasa parangkat lunak sanés, jalma anu bisa ménta inpo data leuwih bakal boga sebutkeun gede dina sakabeh ranté industri. Premis pikeun meunangkeun data gedé tina IoT nyaéta nyetél jaringan terminal anu cerdas kalayan kamampuan ngumpulkeun data aliran ageung..
Skala industri Internet of Things terus tumuwuh
Consumer Internet of Things gaduh prospek pasar anu lega: The White Paper on Kaamanan Terminal tina Internet of Things (2019) nembongkeun yen dina taun panganyarna, aplikasi tina IoT geus mecenghul endlessly, jeung popularization sarta aplikasi médis pinter, angkutan calakan sarta industri lianna geus comprehensively diwanohkeun tumuwuhna éksponénsial tina terminal Internet mahluk. Jumlah alat disambungkeun IoT di dunya ngahontal 11 milyar dina 2019 sarta bakal ngahontal 25 milyar ku 2025. Dibandingkeun jeung 2018, éta ngahontal laju pertumbuhan taunan sanyawa tina 15.71%.
Dina widang konsumen IoT, jumlah sambungan Internet konsumen global tina Hal diperkirakeun tumuwuh nepi 11.4 milyar ku 2025, diantara nu jumlah alat home pinter digambarkeun ku alat kaamanan imah sakuduna dituju nambahan ku 2 milyaran.
Dina watesan ukuran industri, revenues global kayaning produk jeung jasa IoT éta $343 milyar dina 2019 sarta diperkirakeun tumuwuh nepi $1.12 triliun di 2025, kalawan laju tumuwuh taunan tina 21.86%.
Kamajuan téknologi komunikasi, komputasi awan, sarta AI ngarojong ngembangkeun gancang tina industri Internet of Things
Salaku link tina Internet sagalana, ngembangkeun IoT teu bisa leupas tina kamajuan jaringan jeung téhnologi komunikasi. Kusabab watesan transmisi sareng kapasitas komputasi, traditional 4G networks and centralized computing cannot handle the massive data brought by the Internet of Things and cannot realize the idea of real-time interconnection. As new technologies such as 5G, komputasi awan, and artificial intelligence mature and converge, the foundation for the development of the Internet of Things industry has been laid.
5G communication is the latest generation of cellular mobile communication technology. Dibandingkeun jeung 4G, 5G jaringan has the advantages of a higher transmission rate, lower time delay, and more connections, which can meet the higher requirements of network transmission and connection for cloud offices, smart cities and industrial automation. In its 2019 global Exhibition Industry Outlook (GIV@2025), Huawei predicted that by 2025, 58 percent of the world’s population will have ACCESS to 5G networks, 14 persén rumah tangga bakal boga "butlers robot,” jeung 97 persén pausahaan badag bakal ngadopsi AI (kacerdasan buatan).
Komputasi awan ngarujuk kana prosés dimana program komputasi kalayan jumlah data anu ageung dibagi kana sababaraha program anu langkung alit., nu diolah jeung dianalisis ku hiji sistem, sarta hasil itungan dipulangkeun ka pamaké. komputasi awan, salaku komputasi disebarkeun, ngahijikeun langkung seueur sumber daya pangladén sareng gaduh kamampuan ngolah data anu kuat ku ningkatkeun réliabilitas sareng skalabilitas, nyadiakeun solusi pikeun ngolah data masif di jaman Internet of Things. Para ahli ngaramalkeun pasar awan global bakal aya $273.3 milyar dina 2022, ka luhur 212% ti 2016. AI nyaéta élmu anu ngahususkeun kana ulikan intelegensi manusa, sarta ngajadikeun mesin mibanda ciri kecerdasan manusa ngaliwatan simulasi, extension jeung extension. The core of AI is algorithms. Through the improvement of algorithms and computing power, artificial intelligence products have the ability of image processing and language recognition. The global AI market was estimated at us $680 milyar dina 2020, with an average annual growth rate of 32% ti 2015 ka 2020.
Kaayaan pamekaran sareng tren industri parangkat keras Internet konsumen tina Things
Intelligent terminal of consumer Internet of Things refers to terminal hardware products with information collection, processing and connection capabilities, and capable of realizing intelligent perception, interaksi, big data services and other functions. It is an important carrier of artificial intelligence in the Era of Internet of Things and an important link in the industrial chain of consumer Internet of Things. As emerging industries and an important part in the field of consumer electronics, intelligence of the end products such as mobile phones, TV, generasi anyar téhnologi informasi accelerating jeung rumah tangga calakan, hardware otomotif, alat wearable, perlakuan médis mobile jeung saterusna Internet hal integrasi produk terminal calakan, suggesting industri hardware calakan mekar, inovasi mode drive jeung efisiensi.
hardware pinter exploding
Kusabab 2016, Cina parantos berturut-turut ngaluarkeun sababaraha undang-undang, peraturan jeung dokumén kawijakan, kaasup "Aksi Khusus pikeun Inovasi sareng Pangembangan Industri Hardware Intelligent" sareng "Panduan ngeunaan Ngamajukeun sareng Ngatur Aplikasi sareng Pangembangan Kaséhatan sareng Data Médis".
Dina watesan paménta, kalayan tingkat tumuwuhna ékonomi nasional, struktur konsumsi warga terus ningkatkeun, jeung widang jasa saperti hiburan, perawatan médis sarta atikan Usher dina parobahan kontinyu. Luhur-tungtung, produk calakan sarta ngaropéa digambarkeun ku hardware calakan terus mingpin ngembangkeun industri. Dina waktos anu sasarengan, salaku grup konsumen utama di Cina laun-laun ngalih ka generasi post-80s sareng post-90s., standar konsumsi ogé laun-laun ngembang nuju diversifikasi sareng kualitas. produk hardware calakan digambarkeun ku alat wearable, speaker pinter, doorbells pinter jeung saterusna anu lega favored ku pasar.
Dina sisi suplai, kalawan ngembangkeun gancang tina 5G Cina urang, komputasi awan, kacerdasan buatan, Internét tina Hirup jeung industri chip, Cina geus saeutik demi saeutik ngawangun ranté suplai industri hardware calakan lengkep. Jeung deepening gawé babarengan perusahaan, logika produk dasar dina industri hardware calakan bakal terus dihijikeun, jeung gawé babarengan dina r&d, production and sales will become increasingly close. As China matures in the field of information technology, relevant education in colleges and universities continues to be carried out, and the quantity dividend of Chinese engineers will continue to ferment, driving the rapid development of intelligent hardware-related industries.
Gawé babarengan dina industri hardware calakan terus deepen
With the continuous development of intelligent hardware industry, the cooperation between upstream and downstream enterprises of the industrial chain also continues to deepen. In the process of intelligent hardware products, intelligent hardware scheme requires traders and manufacturers from product conception, rarancang, research and development to production and sales of the whole stage, with the telecommunication operation industry chain upstream and downstream enterprises, perusahaan jasa platform damel caket sareng perusahaan ngolah algoritma sareng perusahaan sanés, ngandelkeun kauntungan unggal perusahaan sareng lapangan terus ngawangun kerjasama sadayana, Ngawangun logika dasar produk lengkep, sarta babarengan ngamekarkeun produk hardware calakan pikeun minuhan kabutuhan pamaké.
Dina prosés deepening gawé babarengan ranté industri, gawé babarengan antara algoritma kecerdasan jieunan jeung hardware calakan utamana deukeut. Hardware calakan kalayan akuisisi data optoakustik sareng fungsi ngolah anu diwakilan ku kaméra jaringan calakan, pangrékam data kendaraan jeung headset Bluetooth laun-laun jadi lawang anyar pikeun interaksi manusa-komputer, jeung téhnologi kecerdasan jieunan kayaning pangakuan gambar, face recognition and voice recognition have been applied in industry. With the continuous maturity of industrial chain technologies, the development of artificial intelligence, Internét tina hal, cloud computing and other technologies has greatly promoted the technological upgrading of products, improved product market performance by optimizing product user experience, and become a new hot spot in the industry.
Kisaran aplikasi hardware calakan ngembang pesat
Increasingly rich application scenarios: With the continuous development of artificial intelligence, intelligent hardware products continue to grow and expand to segmented fields and specific scenes. Products tend to be scenario-oriented, and products and services for market segments continue to emerge. Ayeuna, intelligent hardware has been widely applied in smart homes, kota pinter jeung skenario sejenna.





















