Smart warehouse is a storage management concept. It is a smart logistics achieved by IT, IoTs and electromechanics so as to lower storage costs, improve operation efficiency and enhance storage management ability. This article will give you a clear understanding of smart warehouses
1. What is a smart warehousing?
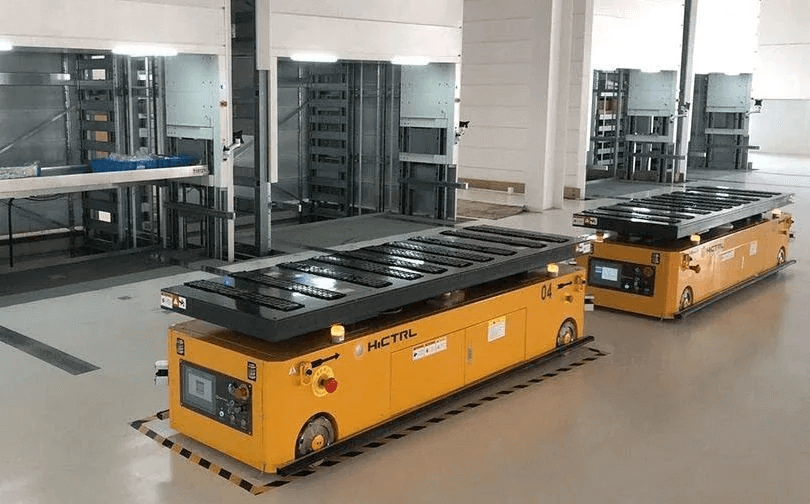

Intelligent storage is one part of the logistics process. The application of intelligent storage keeps fast speed and accuracy of data input in every part of warehouse management. It also ensures that enterprises can understand the actual data of inventory in a timely and accurate manner, so as to reasonably maintain and control the inventory of Companies’ products. The management function of the WMS system is conducive to knowing the current location of all inventory goods in time, which helps improve management efficiency. RFID smart storage solutions are also equipped with RFID channel machines, inquiry machines, readers and much other hardware and equipment.
2. Benefits of Smart Warehousing

1. When the smart warehouse equipment is working, the system automatically receives external orders as well as other orders that need to be dispatched. After that, the equipment automatically finishes the process of storage and takeout of relevant goods. During the whole storage process, there is little dependence that the storage on labor forces, which reduces much more labor costs.
2. Automated machines in intelligent warehouses work more efficiently than manual workers and also keep the efficient operation of the warehouse for a long period of time. Meanwhile, the smart warehouse system is capable of handling much more complicated work, compared to labor forces.
3. Different from traditional warehouses, intelligent storage can not only decrease labor costs and save human resources but also can be utilized in special circumstances like toxic surroundings, extreme weather and higher-level safety protection needs. An Intelligent storage system is a brand new warehousing system that is comprised of various kinds of advanced technologies that can be considered the most advanced science and technology in the storage rack field.
3. Working Principles of Smart Warehousing

The principles of a smart warehousing management system vary in terms of different places. Different works will also result in different working principles:
1. The entry and exit management of a warehouse: UHF readers will be used for warehouse entry and exit management, which can identify the entry and exit of items in a fast manner
2. By using the UHF readers, the Forklift truck is able to quickly and accurately detect whether the goods need to be shipped or not. Also, it ensures the exact shipments of items when the operators are in a hurry working or while there are new operators.
3. Invocation and allocation of Logistics vehicles: the Internet of Things is used to manage the centralized scheduling of logistics vehicles so as to maximize the efficiency of transportation.
4. Readers which are utilized as smart logistics sorting systems can significantly enhance efficiency and guarantee precision.
5. Use hand-held equipment to inspect products and manage assets.
4. What Technologies are used in smart warehousing
RFID
With the help of the automatic identification system which is equipped with the radar reflection principle of the UHF RFID system, the reader sends a microwave query signal to the electronic tag through the antenna. Then readers’ microwave energy can activate the electronic tag. After the reception of the microwave signal, the reader responds and sends out the echoing signal with the tag that includes data information. The fundamental feature of Radio Frequency Identification Technology is to recognize stationary or moving objects using radio technology, with the purpose of ensuring the objects are identified as well as extracting the objects’ feature information (or identification information).
AGV
With the functions of safety protection and all kinds of mobile and loading transport, AGV is transport vehicles that are installed with automated guided devices that are equipped with electromagnets or optics. These kinds of vehicles can be driven following prescribed guided paths. It is an unmanned transport vehicle that is powered by rechargeable batteries and applied in various industries. An AGV is generally monitored by computers to control its travel route and behaviors, or the route can be established by an electromagnetic track. The movement and operation of the unmanned vehicles are controlled by messages conveyed from the electromagnetic track which is attached to the ground.
The Robotic Palletizer
A pallet stack robot refers to a robot that is able to automatically palletize(or dismantle) goods with different dimensions and shapes on the pallet in a neat way. In order to take full advantage of the area of the pallet and ensure the stability of the piling of goods, the robot has been installed with a sequence setting machine that can control the order of goods for piling. Based on the different palletizing mechanisms, robotic palletizers can be divided into two types: multi-layer type and right-angled coordinate type. It can also be categorized by slide-clamp type, bottom-up dragging type and vacuum suctioning type depending on the different forms of clamps.
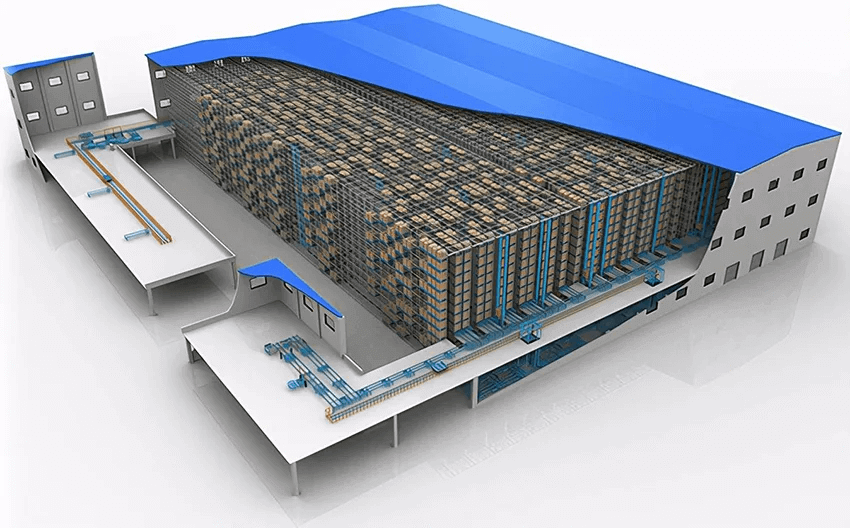
Three Dimensional Warehouse
A three-dimensional warehouse, also known as a high-level shelf storehouse, is called Automatic Storage & Retrieval System (AS/RS). Normally a dozen or even dozens of layers of high selves are included in the warehouse, in which automated transport vehicles handle goods that need to be shipped out and stored. The three-dimensional storage is generally comprised of high-rise shelves, material transport equipment, controlling and management devices, public facilities for land construction, etc.
Warehouse Management System
A warehouse management system (WMS) refers to an information management system that consists of a series of functions including the warehousing business, outbound business, warehouse management, allocation of inventory management, virtual inventory and so on. Using these functions, the storehouse integrates batch management, material corresponding, inventory check-out, quality inspection management, virtual warehouse management and just-in-time inventory management functions into the information system. A warehouse management system effectively controls and tracks the whole process of logistics and cost management of warehouse business to realize the improvement of warehousing information management. The system can perform logistics and warehousing inventory operations independently, and can also improve the intelligent integration of logistics and warehousing with enterprise operation, production, procurement and sales.
Warehouse Control System
The warehouse control system (WCS) is the intermediary between the warehouse management system (WMS) and the logistics devices. The system is in charge of the coordination and schedule of all types of logistics equipment so that the bottom logistics equipment is able to follow up on the business process of the warehousing system. Also, this process is completely executed exactly based on the pre-setting of the program. It functions as a core system to ensure the smooth operation of the entire logistics and warehousing system.
5. What is a smart warehouse system and what are smart warehouse systems
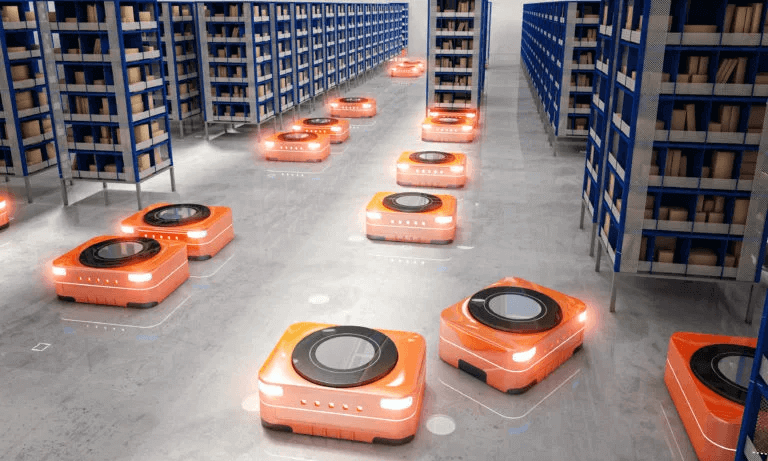

Smart warehouse system is the result of collaborative work of various interconnected warehousing technologies which creates a technical ecosystem that is able to automatically receive, identify, sort, organize and pick up goods. The well-developed smart warehouse solutions can provide almost the automation of the entire operation from supplier to customer with the fewest errors. You should pay more attention to the traits that help mark a successful smart warehouse system while considering smart storage. Some of these traits are:
Agility
The warehouse control system (WCS) is the intermediary between the warehouse management system (WMS) and the logistics devices. The system is in charge of the coordination and schedule of all types of logistics equipment so that the bottom logistics equipment is able to follow up on the business process of the warehousing system. Also, this process is completely executed exactly based on the pre-setting of the program. It functions as a core system to ensure the smooth operation of the entire logistics and warehousing system.
Scalability
SaaS solutions do not encounter this limitation. Updates can be done immediately, and new content can be rolled out without compromising productivity. Implementing new features simply requires bringing in IT to solve unexpected problems, which smart warehouse operators want to deal with.
A smart warehouse should be able to keep pace with future changes and needs as the warehousing and supply chain becomes increasingly complicated. Smart warehouses must be well-prepared for receiving a lot of products and new items releases, which leads us back to the discussion of other traits of the SaaS Solutions.
If you have already come up with plans for internal deployment, it may be difficult for you to add new functions to the smart warehousing system. On some occasions, the whole system is possible to be dismantled after the completion of updates, which possibly leads to the main slowdown operation of the system.
However, SaaS solutions operate without such limitations. The update can be completed in time while the new releases can be launched at the same time, which has no impact on the efficiency. Only the introduction of IT is needed to implement new functions so as to tackle new emergencies, which are the actual issues handled by smart warehouse operators.
Data Visibility
As technology continues to evolve, data visibility has become a necessity for most software that is relevant to the functions of supply. This is of great importance nowadays since supply chain and warehousing operations have more complex changes and instant updates as well as data storage, which should be ready for software solutions. Customers and stakeholders tend to be aware of the exact location of their products based on the real-time data provided by the smart warehouse system.
With smart warehouses, interested parties should be allowed to find what they want in a quick manner. If clients have the option of working with an operation that updates data overnight or keeps it up to date, you can help them make the choice.
This is of great importance when taking into account client retention. In addition, data visibility also provides a wealth of useful information for the operation itself. The operator is given a bird’s eye view of the entire warehouse and the performance of individual components according to the real-time data. If inventory or delivery times are inaccurate, you will know immediately where they come from. In this case, smart warehouse operators can take action before things get under control and put more hands on the job.
6. Smart Warehouse Examples
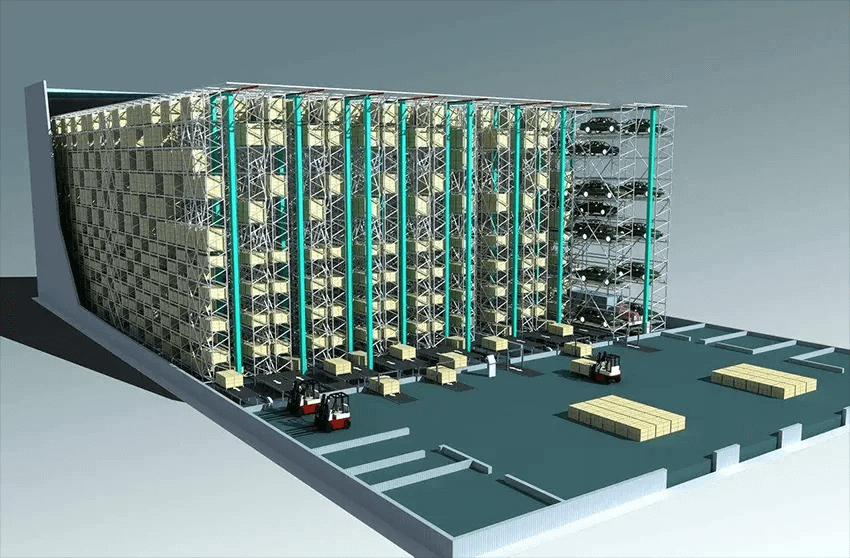

Six common application scenarios for Smart Warehousing System
1. Pharmaceutical warehouse: the storehouse of the Pharmaceutical company contains a large variety of drugs, which need to be managed by the system.
2. Machinery manufacture: 3D warehouses of machine manufacturing plants covers a large production area with large amounts of mechanical products.
3. Tobacco warehouse: tobacco warehouses, embracing lots of items, have strict requirements for the environment so using the storage system gives big hands to manage the environment and goods.
4. Military police force: the munitions warehouse of armed police and military, covering large areas with a large quantity of goods, utilizes three-dimensional shelves.
5. Clothing warehouse: it refers to the garment factories used for the production of children’s & adult clothing.
6. Electronic-commerce warehouse: It stands for those storehouses owned by Amazon, Shopify, eBay and other e-commerce enterprises.
7. History of Smart Warehouse
Traditional manual storage
Manual warehousing works in a way where much manpower is invested to perform storage management and warehousing works. It mainly relies on the working experience of staff to manage the storehouse. What’s more, employees have to go through a long period of training before they are able to do their jobs. In addition, manual storage improves the efficiency of billing records and also reduces the time of making mistakes.
Mechanized storage
During the mechanization stage, the transportation, handling, and management of commodities are no longer purely conducted by manpower but with a combination of mechanical and manual efforts to complete the operations. Items can be transported by conveyors, haulers, cranes, forklifts and other machines. After that, the storage and takeout of goods can be operated by equipment controlled by humans. Mechanical warehousing satisfies various types of needs like precision, quantity, weight, handling and so on. However, as the e-commerce industry and online shopping gain popularity, warehousing and logistics in the mechanization era have faced great pressure.
Automated storage
The transition from mechanization to automation is mainly caused by the growth as well as applications of automation technology. In the 1950s, AGV, automatic shelves and automatic warehousing robots gained popularity one by one and were gradually in widespread use in the warehousing and logistics industry, which brought about the higher working efficiency of the warehousing industry. Since then, automatic identification systems and automatic sorting systems have been researched and developed to make their transit from mechanization to automation. In the 1970s, automated devices like rotated shelves, mobile shelves and laneway palletizers were widely applied in the storage and logistics field while the control and management of computed technologies on the storage operations made the overall benefit far higher the margins before.
Smart storage
The intelligent stage is the further research of the storage industry based on the development of automation. It develops towards the direction of intelligence. The emergence of smart warehousing mainly benefited from the growth of artificial intelligence, in which the data between plates and systems can be mutually shared, providing more convenience to deal with work.
8. The Future Outlook of Smart Warehouse
In recent years, the first echelon of logistics robot enterprises has delivered remarkable achievements. These companies, facing the issues like high renting of warehouses, developed economy, high human resources price and low manual efficiency, are mainly located in typically countries and regions where there are high automation demands of warehousing and logistics. Those countries or regions contain the United States, Europe, Australia, Japan, South Korea and so on.
As the back-end link of smart manufacturing, smart warehousing and logistics undertake great duties like the improvement of efficiency, customer experience and companies’ core competitiveness with the popular concepts of product diversification and customization. Since the technologies like big data, the Internet of things, robots and sensors become more advanced, intelligent storage, functioning as the carrier of the above technologies, is expected to undergo fast growth.
In recent years, with the growth of the warehousing industry, the ratio of the warehousing industry in the total social logistics cost and the proportion of warehousing in GDP has witnessed a fast rise. And the warehousing industry has played a more crucial role in the overall economic operation year by year. Storage facilities are becoming more and more saturated, and the investment in the industry is turning to terminal node construction, information-based operation and intelligence (cloud storage, big data, the Internet of things), resulting in a slowdown in the growth of the investment.
With land utilization and labor cost continuing to increase, storage cost has also experienced a significant increase. Cost reduction and efficiency increase are the core tasks in the future development of the storage industry. Developing smart storage, reducing the use of labor and land, and lowering logistics costs will become
the essential tasks that need to be resolved to achieve the development of the warehousing industry in China.
















