1. What is IoT cold chain?

A type of Internet of Vehicles technology as well with massive data mining, 3G wireless IoT technologies and intelligent remote control as the core means, the smart cold chain is a new generation of operation and management tool that combines the four elements of “people, vehicles, lines and goods” tailored for cold chain vehicles based on the IoT cloud computing platforms and with the integration of intelligence, electronization and information technology. With the combination of intelligent control technologies and the mobile Internet and then the application of the combination in the cold chain, it ultimately realizes intelligent control of the whole cold chain for the products which are delivered from the warehouse to consumers’ homes. With the connection of WeChat and other third-party applications, consumers can monitor the in-transit situations and preservation of their goods in real time on their cell phones. Aucma achieves functions like inventory management, order management, intelligent distribution as well as energy consumption management using the smart cold chain, which can help the company control the changes in the number of goods in transit in real time and substantially boost the working efficiency.
2. What is IoT in supply chain?
Significantly affected by the Internet of Things, the IoT supply chain can help achieve the visibility of the transportation processes. An Analyst firm, Berger Insight, expects that there will be a strong focus on cargo transportation security and the increase in supply chain visibility in the following years. In addition, the tracking of trailers and intermodal containers becoming more prevalent and technological advances enable even smaller logistics units to be tracked at a more reasonable price. The units include individual pallets or cargo boxes.
3. What are the functional processes of a smart cold chain?
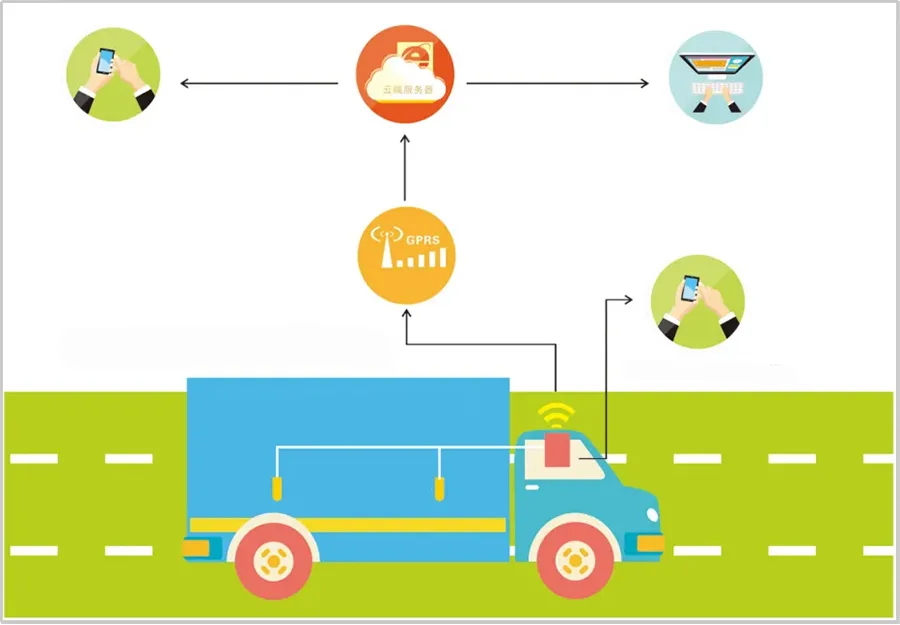
The technical basis for realizing the intelligence of cold chain logistics lies in the use of 5G, Internet of Things, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence, big data, cloud computing and so on. Also, the digitalization level of the cold chain logistics is also a fundamental guarantee to ensure the safety of the entire life cycle of cold chain items, which is conducive to achieving intelligence management of various links of the supply chain involved in the entire life cycle of cold chain items (production, processing, package, loading & unloading, transportation, storage, city distribution, display, destination delivery, etc.).
In the past days, the traditional traceability systems of cold chain food can usually only trace the manufacturing enterprises, which is unable to make the cold chain food traceable to the entire chain of every link. However, with the digitalization of cold chain logistics, the system is expected to truly achieve entire traceability. How can the multi-dimensional state be used to gather data? The answer is mobility (wireless), labeling and multiple functionalities.
First of all, mobility. In order to monitor the third-party logistics temperature control, the system can be equipped with mobile equipment. What’s more, the monitoring equipment needs to be configured with GPS modules. Then with the help of GPS and GIS technologies, the monitoring centers can geographically locate and dispatch the container vehicles. In addition, in cases such as cold chain carriages or cold storage inventories, the temperature at each point is not completely uniform and unified. Therefore, multi-point monitoring becomes a demand point. For instance, the cargoes may not be affected if the temperature against the air outlet is low. However, the situation is different if the cargo is nearby the truck doors.
The second one is labeling. From the workshops to transportation, storage and sales, the goods which are in transit need to be tracked with labels. And the information contained in the labels should be comprehensive including product codes, production origin management, farmer codes and circulation link management so that the safety of the entire cycle of the items can be traced with the support of the labels.
Lastly, multiple functions. An early warning system can be set up. If the change ranges of temperature and humidity are beyond a predetermined range, the system will send an automatic warning. If there is a section of record in the middle of the curve significantly lowering than 20 ℃ in terms of temperature, the corresponding locations and external environments can be queried from the time points of the system in order to explore the reasons for the corresponding temperature and humidity changes. In addition to the collection of temperature and humidity control, the intelligent control of the environment temperature can also realize through software and hardware. For example, the temperature of the cold inventory can be intelligently controlled. The control of the refrigeration systems can be achieved by some control-type labeling equipment and the backend analyzes the cold inventory temperature situation in real time. When temperature control is needed, the system will achieve automatic remote control of the temperature of the refrigerated machine and then applied to stores and transport vehicles.
4. The difficulties facing the smart cold chain

(1) Insufficient refinement of cold chain operation & poor service quality
About 90% of meat, 80% of aquatic products as well as a large amount of milk and soybean products are still basically distributed and sold without the entire cold chain promise. This not only leads to the loss of fresh food but also makes people worry about the quality and safety of fresh food.
(2) The relatively backward development of hardware facilities & inadequate supply of cold chain equipment
The growth of cold chain logistics hardware facilities in developing countries is relatively backward. Take cold storage as an instance: at present, the supply of cold storage is very inadequate. The developing countries have 0.1 cubic meters from the perspective of cold storage per capita, which is far behind compared with 0.3-0.35 cubic meters per capita in Japan and 0.4 cubic meters per capita in the United States.
(3) Lack of standardized management of cold chain logistics leads to increased cost loss
The annual consumption of perishable food exceeds 1 billion tons, of which more than 50% requires cold chain transportation. However, the current comprehensive cold chain circulation rate only reaches 19%, which leads to high rates of decay and loss of agricultural products. The annual loss of fruits and vegetables alone registers more than 100 billion RMB. Due to the lack of standardized management of cold chain logistics, it directly results in additional loss of goods and increased prices of cold chain logistics.
5. The strengths of smart cold chain

Sensor Deployment
One of the key parts of the smart cold chain lies in sensor deployment, which requires tens of thousands of sensors to be embedded in all corners. As a result, the data gathered will be intelligently analyzed using AI to bring physical equipment to life. It can be said that small sensors promote digital changes, allowing everything to be quantified while realizing information collection in processing and other operational aspects.
Intelligent Decision-making
The application of sensors and AI technology allows intelligent decision-making to be more advantageous. The aim of intelligent decision-making is to transform information on cold chain logistics into better actions that can be handled regardless of the scales. It is crucial to use big data technology to identify issues in cold chain transportation and replace relevant experience with knowledge to make intelligence come true.
Automation Control
Data is perfect. However, what should be more perfect is decision making and control. Through the big data algorithms, intelligent and precise decision making can be transferred to the automatic control of cold chain logistics. The special features of cold chain transportation require online monitoring, remote diagnosis, automatic supervision and intelligent control of the equipment.
Transportation Effect & Benefit
The data aggregation or display cannot tackle any pain points. The research and development of intelligent cold chain logistics technologies are to boost the cold chain transportation efficiency by monitoring every link. Thus, it is fundamental to achieve expected results by utilizing intelligent logistics technologies to showcase products, achieve good communication, enhance quality, ensure safety as well as decrease losses.
Online Measures
A prevalent issue in cold chain logistics is the large transportation volume but a low degree of online sales. The transparency of logistics, as well as the transportation collection of cargo owners are highly low and the volatility of the price is relatively large. In addition, the service guarantee is insufficient. Thus, all kinds of resources should be fully integrated and optimized. Also, the maximum use of Internet technologies can help break through so that the cold chain circulation becomes more efficient, more transparent and more secure.
6. What are the fields being applied with the smart cold chain?
Enterprises that focus on cold chain storage fields are mainly engaged in the processing, storage and transportation of fresh vegetables, meat, seafood, meat and frozen food. Mobile intelligent terminals, the data collection terminal equipment, are mainly applied in various links such as the cross-warehouse distribution of commodities, fleet management as well as pick-up of goods to realize data-based functions, informationization and digitization of the cold chain storage working processes. Therefore, these are the vital operational tools necessary for workers in cold chain storage.
(1) Fleet Management
Through the locating system and data collection as well as the record of mobile intelligent terminals, employees are able to realize real-time monitoring of the locations and statuses of all assets in the process of cold chain transportation to achieve digital management and control of the fleet, thus ensuring accurate delivery of goods to customers.
(2) Regular Stocking
By using the mobile intelligent terminals, workers are able to collect and record all the statuses and information of all goods in the warehouse throughout the whole process from the warehousing and shelves to the shipment. Then the statuses and information can be uploaded to the system backstage in a synchronized way. Thus, personnel who is in charge of the inventory can view the system to learn about the current inventories in the warehouse to complete the stocking as well as inventory analysis and management, thus boosting the productivity of the warehouse.
(3) Stock preparation and shipment
Personnel who is responsible for the delivery of goods scan and confirm orders through mobile intelligent terminals, using the label printers to print accurate destinations for shipping labels to achieve fast shipment. At the same time, recording the shipping status will be recorded in the system backend so that the relevant information can be read and utilized for the next logistics link.
(4) Task Collection
Working staff receives and collects tasks directly on the mobile smart terminals at any time and location. After that, the terminals can be quickly scanned to record the information as well as weight and calculate the size. The electronic signature function of the mobile intelligent terminal can be used to sign names to ensure the handover, realizing rapid parcel collection and distribution.
(5) Return of Goods
Through mobile smart terminals, staff can make sure that every returned parcel is able to be processed in a timely and efficient manner. The mobile smart terminal will scan and record the status of returned goods upon receipt to ensure that they are put back into the warehouse for the purpose of refurbishment or the stop of use.
7. What are the technologies being used in the smart cold chain?

- In-warehouse Technology
Robots, as well as automated pickup & sorting technologies have been well-developed and in wide applications. There are four main types of technologies, including robotics and automated pickup & sorting, wearable devices, driverless forklifts and goods recognition. All of them are applicable for operations like in-warehouse handling, shelving as well as sorting. Some foreign companies which have taken the lead in these areas have employed these technologies at an early stage and have started commercialization. Enterprises abroad such as Amazon and DHL Express, and domestic companies such as JD, Cainiao and Shentong have already planned their business in the field.
- Mainline Technology
Mainline technologies mainly stand for driverless truck technologies. The changes in the existing patterns of the mainline logistics will take place with the help of the driverless trucks, which have still been under the research and development process but have achieved good results. Currently, the technology is being tested before putting into commercialization.
- Technologies of Last Mile
The technologies of Last Mile mainly cover 2 major categories. They are drone technology and 3D printing technology. Being in a well-developed stage, the drone technology has been tested commercially in domestic and foreign logistics enterprises including JD, SF, DHL Express and so on. 3D technology has been in the research and development stage. Only Amazon, UPS and other enterprises have developed the technical aspects.
- End-end technology
The new end-end technology primarily refers to the smart express cabinets, which are an essential part of the technical layout of major enterprises. Currently, the technology has been covered commercially in first- and second-tier cities. However, there will be a lot of uncertainties for the future development of the technology due to the issues like the limited cost and the usage habits of clients.
- Smart Data Bases
The database mainly consists of 3 major areas with the coverage of IoT, big data and artificial intelligence. IoT technology and big data analysis techniques provide support to each other, which represents that the IoT technologies provide parts of the analysis data sources for the big data analysis technology while the latter operationalizes the data of the former one. However, artificial intelligence is the improved version of big data analysis. Through the collection and analysis of commodity flow and logistics data, the big data analysis technology is mainly utilized in areas like demand estimation, storage network, router optimization as well as equipment maintenance warning, which are vital focuses for the growth of intelligent logistics in the future as well as the key to the issue that whether intelligent logistics can be further upgraded and iterated.
















