Dit artikel geeft u een uitgebreid overzicht van WIFI-technologie en haar toepassingen, oplossingen, en veelgestelde vragen over het internet der dingen.
In het tijdperk van het internet der dingen, wanneer machines moeten communiceren, Dat doen ze in een taal waarin ze elkaar kunnen begrijpen. Dat is draadloze communicatietechnologie.
Tot de draadloze communicatietechnologieën op korte afstand die veel worden gebruikt in het internet der dingen behoort WiFi (IEEE 802.11 protocol), Gaas, Bluetooth, ZigBee, NFC, UWB, enz. De WiFi-module met brede dekking en snelle gegevensoverdracht is duidelijk de lieveling van de draadloze communicatietechnologie in het Internet of Things. Vooral bij de intelligente thuisterminalproducten komt de toepassing vaker voor.
Wat is WIFI-technologie?

Wifi, de Engelse volledige naam is Wireless Fidelity, namelijk Wireless Fidelity-technologie. Het is een technologie die draagbare apparaten en pc's draadloos met elkaar verbindt.
Wi-Fi is een merk van draadloze netwerkcommunicatietechnologie om de interoperabiliteit tussen draadloze netwerkapparaten te verbeteren.
Internationale transportprotocolstandaard
Momenteel, WLAN-veld is voornamelijk de IEEE802.11x-serie en de HiperLAN/X-serie van twee standaarden, evenals de Chinese WAPI-standaard.
802.11 is voor draadloze netwerkcommunicatie. Deze standaard is sindsdien verbeterd om de 802.11x-standaardfamilie op te zetten. 802.11x is de technische basis van Wi-Fi.
WAPI-standaard
WAAR, Draadloze LAN-authenticatie en privacy-infrastructuur(WLAN-authenticatie en privacy-infrastructuur) is een beveiligingsprotocol ontwikkeld door de China Broadband Wireless IP Standard Working Group. Het is ook een verplichte beveiligingsstandaard voor draadloos LAN in China, goedgekeurd door THE IEEE Registration Authority en geautoriseerd door ISO/IEC. Deze standaard is een beveiligingscoderingsstandaard gerelateerd aan IEEE802.11b, maar het is niet compatibel met de reguliere WEP en WPA die zijn geformuleerd door de Wi-Fi Alliance. Het is vergelijkbaar met het huidige 802.11i-transmissieprotocol.
Technologie voor gegevenscodering
Vanwege de bijzonderheid van de fysieke topologie, draadloze netwerken kan het beveiligingsniveau van bekabelde netwerken niet bereiken. Daarom, encryptie en authenticatie zijn veiligheidsoverwegingen in draadloze netwerken. Het fundamentele doel van het gebruik van encryptietechnologie in draadloos LAN is ervoor te zorgen dat draadloze diensten hetzelfde beveiligingsniveau bereiken als bekabelde diensten.
2. Soorten WiFi-technologie

1. WLAN
Een WLAN is een LAN dat gegevens draadloos verzendt en ontvangt, zonder netwerkkabels.
2. AP
Toegangspunt (draadloos toegangspunt), het apparaat is het kernapparaat in een draadloos LAN, voornamelijk gebruikt om verbinding te maken met bekabeld Ethernet, zoals internet, en draadloze signalen uitzenden. Binnen een bepaald dekkingsgebied, het signaal van het AP kan worden ontvangen via een draadloze netwerkkaart.
3. SSID
SSID kan een draadloos LAN in verschillende subnetwerken verdelen. Voor elk subnetwerk is onafhankelijke authenticatie vereist. Als u het overeenkomstige subnetwerk wilt invoeren, dan moet u een geverifieerde gebruiker zijn. Voorkom dat ongeautoriseerde gebruikers toegang krijgen tot het netwerk.
4. RSSI
Ontvangen signaalsterkte-indicatie verzendt een laag die wordt gebruikt om de kwaliteit van een verbinding te bepalen en of de intensiteit van een uitzending moet worden verhoogd.
5.WPS
Wi-Fi beveiligde instelling (Wi-Fi beveiligde instelling) is een optioneel authenticatieprogramma georganiseerd door de WiFi Alliance om de installatie en codering van het draadloze netwerk te vereenvoudigen. In het algemeen, wanneer een gebruiker een draadloos netwerk aanmaakt, om de veiligheid van het draadloze netwerk te garanderen, de gebruiker stelt de naam van het draadloze netwerk in (SSID) en draadloze coderingsmodus, dat is, “Verberg de SSID” of “wachtwoord voor draadloze netwerkverbinding”. SSID en draadloze coderingssleutels kunnen automatisch worden geconfigureerd met WPS.
In dit gedeelte worden de belangrijkste Wi-Fi-technologieën beschreven 6
Wifi 6 is een evolutie van de vorige generatie WiFi-technologie. Het protocol heet 802.11ax, en de operationele band is 2,4 GHz + 5GHz wifi-technologie. Wifi 6 heeft een grotere single-stream bandbreedte, maximale modulatie, MCS-bereik en compatibiliteit met up-en-down MU-MIMO en OFDMA in vergelijking met de huidige populaire WiFi-technologieën. Alle geavanceerde MIMO-functies van Wi-Fi 5 worden geërfd door Wi-Fi 6 terwijl veel nieuwe functies worden toegevoegd voor implementatiescenario's met hoge dichtheid.
Wifi 6 heeft een aantal belangrijke nieuwe functies
01. OFDMA frequentieverdelingsmultiplextechnologie
OFDMA is voortgekomen uit OFDM en werd voor het eerst toegepast in de communicatietechnologie. Het wordt ook gebruikt in de Wi-Fi 6 standaard om het spectrum efficiënter te maken. Op de traditionele manier, elke gebruiker verzendt gegevens (ongeacht de grootte van het pakket) zal het hele kanaal bezetten. Omdat er in het draadloze netwerk een groot aantal beheerframes en besturingsframes wordt verzonden, deze frames beslaan het hele kanaal, ook al is het pakket klein, net als een grote bus met slechts één passagier, zoals weergegeven in de onderstaande afbeelding:
OFDMA draadloze kanaaltechnologie zal verdelen (een vervoerder), meerdere subkanalen vormen een frequentiebronblok, gebruikersgegevens die betrekking hebben op elk resourceblok, in plaats van het hele kanaal in beslag te nemen, om meerdere gebruikers tegelijkertijd parallelle transmissie binnen elke tijdsperiode te realiseren, niet in de rij staan, met elkaar concurreren, de efficiëntie vergroten, het verminderen van de wachtrijvertraging.
02. DL/UL MU – MIMO-technologie
802.11AC Wave2 beschikt over Downlink Mu-MIMo omdat het AP-knooppunt tegelijkertijd datapakketten naar meerdere mu-MIMO-clients kan verzenden, waardoor het probleem wordt geëlimineerd dat draadloze APS slechts met één terminal tegelijk kan communiceren.
Wifi 6 neemt deze technologie en bouwt erop voort, ondersteunt het verzenden van gegevens naar maximaal acht terminals tegelijk. Uplink Mu-MIMo wordt ook ondersteund op Wi-Fi 6, waardoor maximaal acht 1×1-gebruikers gelijktijdig kunnen uplinken.
03. Modulatietechnologie van hogere orde
Het 802.11ax-standaarddoel om de latentie te verminderen, efficientie verbeteren, en verhoog de systeemcapaciteit in scenario's met hoge dichtheid voor meerdere gebruikers. Echter, hogere efficiëntie en hogere snelheid sluiten elkaar niet uit. 802.11AC maakt gebruik van 256-QAM orthogonale amplitudemodulatie, die uitzendt 8 bits gegevens per symbool (2^8=256). 802.11AX maakt gebruik van 1024-QAM orthogonale amplitudemodulatie, die uitzendt 10 bits gegevens per symboolbit (2^10=1024). De stijging van acht naar tien is 25%, wat betekent dat 802.11ax een 25% toename van de single-stripe datadoorvoer vergeleken met 802.11AC.
Orthogonale amplitudemodulatiedemonstratie van drie verschillende technieken
04. Multiplexing van ruimteverdeling
Er kan slechts één gebruiker tegelijk gegevens overdragen op een kanaal. Het vermijden van botsingen wordt automatisch geïmplementeerd en de verzending wordt vertraagd als het Wi-Fi-toegangspunt en de client naar anderen luisteren 802.11 radio-uitzendingen op hetzelfde kanaal. Vandaar, elke gebruiker moet om de beurt de wifi-radio gebruiken. Vandaar, het kanaal is een zeer nuttige hulpbron in het draadloze netwerk.
802.11ax kan in de 2,4GHz- of 5GHz-band werken (in tegenstelling tot 802.11ac, het kan alleen in de 5GHz-band werken). Er kunnen ook te weinig beschikbare kanalen optreden bij implementatie met hoge dichtheid. De doorvoercapaciteit van het systeem zal worden vergroot als de kanaalmultiplexmogelijkheid wordt verbeterd.
Contrast 802.11AX met 802.11AC-technologie
Vergeleken met 802.11AC (Wifi 5), 802.11bijl (Wifi 6) maakt WLAN-netwerk “efficiënt” via DL/UL OFDMA, UL MU-MIMO en ruimtemultiplexing. De snelheid wordt verhoogd tot 9,6 Gbps door modulatieverbetering zonder tegelijkertijd de bandbreedte en het stroomaantal te vergroten.
3. Hoe werkt WiFi

Zoals traditionele transistorradio's, WiFi-netwerken maken gebruik van radiogolven met een langere golflengte in het elektromagnetische spectrum dan infrarood licht om informatie via de lucht te verzenden.
WiFi-radiogolven hebben doorgaans een frequentie van 5.8 GHz en 2.4 GHz. Deze 2 WiFi-banden worden vervolgens onderverdeeld in meerdere kanalen.
Een draadloze router ontvangt eerst gegevens van internet via uw breedbandinternetverbinding en zet deze vervolgens om in radiogolven. De draadloze router zendt vervolgens radiogolven uit in de omgeving.
WiFi-netwerken kunnen worden verstoord door interferentie van andere elektronische apparaten of WiFi-netwerken, omdat WiFi afhankelijk is van radiogolven.
Om de beste WiFi-prestaties te garanderen, netwerkbeheerders wenden zich vaak tot WiFi-analyser-apps zoals NetSpot om deze te bekijken, beheren, en problemen met WiFi-verbindingen oplossen. NetSpot produceert WiFi-netwerk, gebieden markeren waar het signaal zwak is. In het huidige alomtegenwoordige WiFi-tijdperk, Tools zoals NetSpot zijn essentieel voor het opzetten van zelfs eenvoudige WiFi-thuisnetwerken.
4. Vergelijking tussen WiFi-technologie en Bluetooth-technologie

Als je WiFi en Bluetooth vergelijkt, wat zijn hun overeenkomsten en verschillen? Stel je voor: technologieën als deze zullen nooit bestaan, het zou een wereld zijn van tijdrovende inbelverbindingen, schijnbaar eindeloze downloads, langzaam ladende webpagina's, en eindeloze draden die meerdere apparaten verbinden. WiFi en Bluetooth zijn noodzakelijk in onze verbonden wereld. Ons dagelijks leven wordt op veel gebieden beïnvloed.
Heeft Bluetooth WiFi nodig?? Nee, dat is niet het geval
Bluetooth zelf is niet afhankelijk van een internetverbinding, hoewel sommige apparaten mogelijk over WiFi- en Bluetooth-mogelijkheden beschikken. WiFi en Bluetooth verbinden elektronische apparaten draadloos. Echter, hun activiteiten zijn verschillend. Laten we verder lezen.
Begrijp de WIFI
WiFi is een draadloze technologie waarmee apparaten via WiFi-routers verbinding kunnen maken met internet. WiFi-signalen worden door internetproviders doorgegeven aan routers om apparaten zoals tablets mogelijk te maken, laptops, computers, en telefoons die via internet toegankelijk zijn. WLAN kan door deze apparaten worden gecreëerd. Het netwerk varieert van 150 naar 300 voeten.
WiFi zelf is nieuw, terwijl de geschiedenis van internet teruggaat tot de oprichting van het ARPANET door het Amerikaanse ministerie van Defensie in de jaren zestig. Het werd aan consumenten geïntroduceerd als “WiFi 1” in 1997 met de PUBLICATIE van IEEE 802.11, een LAN-standaard.
De non-profit WiFi Alliance werd opgericht in 1999. De WiFi Alliance certificeert nieuw geproduceerde WiFi-apparaten door tests uit te voeren op andere apparaten die met WIFI zijn verbonden. Beschouw interoperabiliteit als het vermogen van 2 of meer apparaten om naadloos te werken zonder elkaar te storen.
De behoefte aan snelheid
Terwijl de originele WiFi-routers op draaiden 2.4 GHz (2.4 miljard golven per seconde), sommige WiFi-routers draaien tegenwoordig op 3.6 GHz of 5 GHz. 5GHz-routers kunnen een doorvoersnelheid van 3,5Gbps bereiken (gigabit per seconde), terwijl de volgende generatie 6GHz-routers het potentieel hebben om te werken 250% sneller met 9,6 Gbps. Wifi 6 biedt een hogere netwerkefficiëntie, langere levensduur van de batterij, en snellere gegevensoverdracht.
Internetsnelheid wordt steeds belangrijker omdat steeds meer huishoudens het aantal aangesloten apparaten in hun netwerk uitbreiden. Dus hoe belangrijk is het om WiFi te versnellen?
Begrijpen van Bluetooth
Bluetooth verbindt apparaten rechtstreeks met elkaar, in plaats van via WiFi-routers. Bluetooth werkt als een korteafstandsradio. Het kan verbinding maken met meer dan 8 verschillende apparaten na het verzenden en ontvangen van gecodeerde gegevens via een ingebouwde computerchip in het apparaat.
Via Bluetooth verbind je je toetsenbord draadloos met je laptop, bedien het volume van je speakers via een app op je telefoon, verbind uw telefoon met het geluidssysteem van uw auto, en meer.
Hoe verhoudt Bluetooth zich tot WIFI??
Bluetooth heeft een veel korter bereik en een veel langzamere overdrachtssnelheid in vergelijking met WiFi. Dat betekent dat Bluetooth-batterijen langer meegaan en lang niet zo lang duren. Dat maakt Bluetooth-apparaten zo klein.
Bluetooth is ontworpen om kabels en draden te elimineren. dr. Nils Rydbeck introduceerde het eerste Bluetooth-protocol via een handsfree hoofdtelefoon 1999 met dr. Johan Ullman en dr. Jaap Haartsen.
SIG is opgericht door Nokia, Ericsson, Toshiba, Intel, en IBM in november 13, 2000.
Bluetooth en WIFI
Zoals WiFi, Bluetooth draait op 2.4 GHz. Bluetooth kent geen signaalinterferentieproblemen in het 2,4GHz-spectrum. Babyfoons, garagedeuropeners, elektronisch speelgoed, draadloze oordopjes, Magnetrons gebruiken allemaal de frequentie van 2,4 GHz.
Hoe omzeilt Bluetooth deze interferentie??
Bluetooth maakt gebruik van FHSS, die signalen overdraagt die alleen kunnen worden gedecodeerd door het Bluetooth-apparaat dat ze verzendt en ontvangt. FHSS-signalen wisselen elkaar af 79 verschillende kanalen.
De FHSS-technologie van Bluetooth is de reden dat u zonder enige interferentie op een draadloos toetsenbord kunt typen en via een draadloos oordopje met een draadloze muis naar uw telefoon kunt luisteren. Dit netwerk van Bluetooth-apparaten is Piconet. Het Bluetooth-protocol in het apparaat bepaalt wie het master- en slave-apparaat is.
Er vindt onmiddellijk een elektronisch gesprek plaats wanneer u een draadloos Bluetooth-apparaat “koppelt”. Of gegevens gedeeld moeten worden, gesprekken zijn bedoeld om vertrouwen tussen apparaten op te bouwen en beslissingen te nemen. Bluetooth FHSS-technologie zorgt ervoor dat uw piconet geen interferentie veroorzaakt met andere micronetten in dezelfde omgeving.
WIFI en Bluetooth: een betere combinatie
WiFi elimineert bellen, terwijl Bluetooth kabels elimineert. Beide zijn complementaire radiofrequentieapparaten. Iedereen kan ons helpen in realtime verbonden te blijven, productiever zijn op het werk, en geniet van onze vrije tijd. We zijn er zo aan gewend geraakt dat we afhankelijk zijn van zowel Bluetooth als WiFi, dat de oude inbelverbindingen en draad uit het verleden slechts een verre herinnering zijn.
5. WIFI 6 is voorgesteld

Wat is Wifi6?
Wifi 6 is de nieuwste standaard voor draadloze communicatietechnologie 802.11ax die is uitgebracht in 2019. Het is een nieuwe naamgevingsmethode ontwikkeld door de WiFi Alliance. Tegelijkertijd, voor het gemak van het geheugen, de vorige generaties vereenvoudigden ook de naamgeving:
We gebruiken nu vaak 802.11AC – WiFi 5
802.11n — WiFi 4
3-802.11 g WiFi
802.11 – de wifi 2 A
802.11 – de wifi 1 B
Wat is er zo goed aan Wifi6?
Snelheid is snel
Vergeleken met de vorige generatie WiFi5, Wifi 6 kan theoretisch verzenden met maximaal 9,6 Gbps, bijna driemaal zo hoog.
Dit betekent dat onder de nieuwe standaard, je zult nooit het gevoel hebben vast te zitten in het echte leven (bestand, bekijk video). Echter, je hebt wifi nodig 6 ingeschakeld apparaat eerst.
De bovengrens van de netwerksnelheid is verhoogd
Vergeleken met WiFi 5, Wifi 6 standaard verbetert de MU-MIMO-technologie verder en ondersteunt uploaden en downloaden (Wifi 5 ondersteunt alleen mu-MIMO tijdens het downloaden) om het bandbreedtegebruik van draadloze netwerken te verbeteren. In aanvulling, Er worden maximaal acht antennes ondersteund om gegevens te verzenden, waardoor de bovengrens van de netwerksnelheid aanzienlijk wordt verhoogd.
Verlicht netwerkcongestie
Wifi 6 maakt gebruik van OFDMA (orthogonale frequentieverdeling meervoudige toegang) technologieën om de netwerkcapaciteit te vergroten en datacongestie en vertraging effectief op te lossen.
Bijvoorbeeld, in het verleden, WiFi was een supermarktkassa, die slechts de vergoeding van één persoon tegelijk kon verwerken, terwijl die achterwerken alleen maar in de rij konden wachten. Wifi 6, die gebruik maakt van OFDMA-technologie, is als meerdere kassa's in supermarkten die tegelijkertijd de rekeningen van meerdere mensen kunnen afhandelen. Ook dit levert een grote efficiencyverbetering op.
Veiliger
Te certificeren door de WiFi Alliance, Wifi 6 apparaten moeten WPA3 gebruiken, dus de meeste WiFi 6 apparaten zullen veiliger zijn zodra het certificeringsprogramma van start gaat. (Uit Baidu Encyclopedie)
Dit betekent dat wanneer we draadloze netwerken gebruiken op openbare plaatsen zoals luchthavens en coffeeshops, Dankzij WPA3 kunnen hackers niet in onze gegevens snuffelen.
Verbeter de levensduur van apparatuur
Wifi 6 introduceert ook Target Wake Time (TWT) technologie, waardoor de draadloze router de verbinding alleen kan openen wanneer het transmissiecommando wordt ontvangen, en ga dan slapen om het energieverbruik te verminderen. Echter, mobieltjes, laptops en andere apparaten hebben constante toegang tot internet nodig, dus TWT-technologie is niet duidelijk op deze apparaten; En voor nu, populair smart home kan de levensduur van de batterij aanzienlijk verbeteren.
conclusie
Simpel gezegd, Wifi 6 is de 6e generatie draadloze netwerktechnologie. Vertrouwen op technologische innovatie, het heeft de transmissiesnelheid aanzienlijk verbeterd, communicatie kwaliteit, toegang tot meerdere apparaten en beveiliging van een draadloos netwerk. Met WiFi 6 ingeschakelde routers, Wifi 6 ingeschakelde mobiele telefoons, computers en andere draadloze apparaten, en gigabit breedband, je zult een vliegende internetervaring hebben.
6. Waarom WIFI
Er wordt voorspeld dat het voorbij is 5 miljard verbonden apparaten tegen het einde van dit jaar. Gebrek aan standaardisatie, veiligheid, batterijduur, integratie, en snelle groei zijn uitdagingen waarmee IoT wordt geconfronteerd. Zojuist 16 jaar oude WiFi is klaar voor IoT, wat waarschijnlijk het beste netwerk voor IoT is.
IoT is tegenwoordig misschien wel het modewoord, maar de zoektocht naar verbonden dingen is niets nieuws. AutoID, aangesloten Coca-Cola-automaat, M2M, Beller ID, slimme meter, RFID, etc. De aantrekkingskracht van verbonden apparaten is efficiëntie en ervaring, waar mensen meer dan ooit naar verlangen. We leven in een tijdperk van ervaringen waarin geduld schaars is en we willen dat de dingen om ons heen ‘goede ervaringen’ en ‘efficiënt’ zijn, en alleen IoT kan dat waarmaken. IoT is een intelligent en onzichtbaar netwerk waarbij zaken direct of indirect met elkaar verbonden zijn voor beleving en efficiëntie.
IoT wordt geconfronteerd met uitdagingen, zoals hieronder:
Wordt gebruikt om apparaten of cloud computing aan te sluiten
Apparaten in het Internet of Things hebben vaak een vorm van ingebedde technologie waarmee ze zaken als druk kunnen waarnemen, vochtigheid, temperatuur, beweging, en het aantal mensen in de omgeving. En dan is er nog een technologie waarmee ze verbinding kunnen maken met cloud computing of andere apparaten waarmee ze die informatie kunnen verzenden en programmeren. Er zijn veel eigen technologieën en standaarden voor het verbinden van apparaten of het verbinden met de cloud: Bluetooth, Wifi, ZigBee, Actieve RFID, IoWPAN, EtherCAT, NFC, enz. De voorkeurstechnologie wordt doorgaans bepaald door de fysieke eigenschappen van de omgeving, zoals hout, concreet, metaal, enz. Van deze technologieën, Wi-Fi is het meest veelbelovend. Nu is Wi-Fi de standaard geworden voor de populariteit van internet. Het wordt gebruikt in huizen, ondernemingen, scholen, ziekenhuizen, luchthavens enzovoort.
Maar alle actieve RFID-technologieën die lager werken dan de 1GHz-band worden ook gebruikt voor connectiviteit omdat het aantal apparaten van het apparaat naar het toegangspunt beperkt is. Een groot aantal apparaten en een veel groter bereik worden mogelijk gemaakt door actieve RFID-technologie.
802.11ah wordt ontwikkeld om de 900MHz-band te benutten, waarmee tegemoet wordt gekomen aan de noodzaak om een groot aantal apparaten over lange afstanden met elkaar te verbinden. Een typisch 802.11ah-toegangspunt kan verbinding maken 8,000 apparaten binnen een straal van 1 kilometer, waardoor het ideaal is voor netwerkomgevingen met hoge dichtheid. De Wi-Fi Alliance belooft de standaard binnenkort uit te rollen. Na de lancering van deze standaard, Wi-Fi zal waarschijnlijk de voorkeurstechnologie voor IoT worden.
En, herinneren, de ontwikkeling van het IoT is nog maar net begonnen. Wij groeien snel, maar er zijn veel onzekerheden in de toekomst. Vooruit gaan, de beste aanpak is het gebruik van gemeenschappelijke mondiale standaarden voor het internet der dingen en applicatieprogrammeringsinterfaces, zodat deze apparaten met elkaar kunnen communiceren en verbinding kunnen maken met de cloud zonder de netwerkinfrastructuur te upgraden. Standaardisatie en interoperabiliteit zijn een van de belangrijkste redenen waarom Wi-Fi zo populair is, en nog een reden waarom iT past bij het Internet of Things.
Beveiligings- en privacyvereisten die door IoT worden veroorzaakt
Het Internet of Things heeft een wereld zonder grenzen gecreëerd waarin alles kan communiceren met cloud computing. Apparaat- of netwerkbeheerders kennen misschien niet eens het besturingssysteem of het firmwaresysteem van die apparaten of de cloud computing-applicaties waarmee ze communiceren. Het is een uitdaging om de privacy te beschermen en kwaadaardig gedrag te voorkomen.
Beheerders weten mogelijk niet welke andere informatie deze apparaten zullen verzenden of hoe die informatie zal worden gebruikt. Te veel cloudapplicaties, te veel API's, en te veel aanvallers. SDN is de meest natuurlijke oplossing voor beveiligings- en privacyproblemen, en in de afgelopen jaren, de industrie heeft vooruitgang geboekt bij de implementatie van WiFi rond SDN(Softwaregedefinieerde netwerken). Met SDN, Wi-Fi kan een uniform beleidsbeheer realiseren, zodat IoT-apparaatverkeer kan worden gescand en beschermd op netwerktoegangspunten.
Zonder energie-efficiëntie, de kosten voor het onderhoud van de apparatuur zouden te hoog zijn
Omdat de meeste van deze apparaten verwijderbaar of zelfonderhoudend moeten zijn, verlengd batterijvermogen is een noodzakelijk iets. Batterijen kunnen niet elke paar dagen of weken worden vervangen, en het is het beste om zonne-energie te gebruiken, wind, warmte en elektriciteit. Er zijn in de sector veel inspanningen geleverd om Wi-Fi energiezuiniger te maken, en veel leveranciers richten zich nu op Wi-Fi-chipsets met laag vermogen. In aanvulling, 802.11ah kan bijdragen aan een laag stroomverbruik, waar de nieuwste innovaties op het gebied van verspreide Wi-Fi kunnen worden gebruikt om Wi-Fi met een laag energieverbruik te bereiken zonder stroom of batterijondersteuning.
Globaal genomen, gezien het potentieel om al deze uitdagingen op te lossen, Wi-Fi lijkt de meest geschikte keuze voor het Internet of Things.
7. Voor- en nadelen van WIFI Internet of Things

Voordelen van WiFi-netwerk
Draadloze netwerken bieden veel mogelijkheden en de vrijheid om de toegankelijkheid en het internet te gebruiken. Welk apparaat u ook gebruikt, u moet over een draadloze router en ontvangerantenne beschikken. Hier zijn enkele voordelen van kennis over WiFi via bekabelde netwerken.
Handig WiFi-netwerk
Meerdere gebruikers kunnen verbinding maken met een router of via hotspot-technologie zonder enige configuratie via een draadloos netwerk. Het is gemakkelijk te gebruiken. Deze mogelijkheid om verbinding te maken via een draadloos netwerk vervangt effectief bekabelde of bekabelde netwerken, die meer tijd vergen om verbindingen te configureren en toe te staan in omgevingen met meerdere gebruikers.
Flexibiliteit op het werk
Een van de voordelen van WiFi is de flexibiliteit die het biedt op de werkplek. Blijf niet op één plek en werk. Soms kan het lastig zijn om een RJ-45- of netwerkkabel te vinden die u op een desktop of desktop kunt aansluiten. Een op de werkplek geïnstalleerd WiFi-apparaat biedt service voor elke gebruiker, waardoor de workflow zonder enige belemmering kan doorgaan.
Productiviteit verhogen
Werknemers kunnen hun werk gemakkelijk volhouden omdat ze geen tijd hoeven te verspillen met LAN-verbindingsproblemen of serverproblemen. Als meerdere gebruikers toegang hebben tot hetzelfde netwerk, IP-adresconflicten zijn het minst waarschijnlijk. Werk kan overal worden uitgevoerd, van het versturen van e-mails tot het verkopen van bijeenkomsten. Dit kan ook de productiviteit beïnvloeden bij het behalen van doelen en op tijd werken.
WiFi zorgt voor mobiliteit
Kan overal werken, van de cabine tot de cafetaria, zonder dat u achter een computer hoeft te zitten om taken uit te voeren. Dingen kunnen ook worden geautomatiseerd via uw telefoon. De WiFi-verbinding maakt het mogelijk om transacties via mobiele apparaten uit te voeren, omdat de technologie werkt met elk slim apparaat dat kan worden geïntegreerd met het omliggende WiFi-netwerk. U kunt banktransacties verzenden, e-mails, en werkrapporten bekijken terwijl u onderweg bent.
WiFi is eenvoudig te implementeren op de infrastructuur
Eén WiFi-toegangspunt is goed voor het wegwerken van plannen en kaarten voor het leggen van kabels en schakelaars op de werkplek. Bedenk dat de nieuwe cabine van zijn huidige positie is verplaatst en dat er een nieuwe aansluiting moet worden geïnstalleerd. Het in kaart brengen en installeren van complexe bekabelde netwerken kan lastig zijn vergeleken met het installeren van draadloze apparaten in de cabine.
WiFi is kosteneffectief
Het voor de hand liggende voordeel van een draadloos LAN is dat de kosten voor het bouwen van een nieuw netwerk minimaal zijn. De bekabelingskosten kunnen worden verlaagd, arbeidskosten kunnen worden verlaagd, en tijd bespaard, en vooral omdat bij het proces alle drie de factoren betrokken zijn die van invloed zijn op het nieuwe organisatiebudget van het bedrijf.
Uitbreidingen en toevoegingen
Nieuwe gebruikers kunnen op elk moment aan het WiFi-netwerk worden toegevoegd. Het verlenen van toegang aan gebruikers met draadloze LAN-referenties om hen geautoriseerde gebruikers te maken, is wat u moet doen. De tijd en moeite die gemoeid is met het bedraden van gebruikers zal worden geminimaliseerd en er zullen connectoren worden toegevoegd.
Draadloze LAN's zijn eenvoudig te verplaatsen
Draadloze LAN-netwerken zijn eenvoudig te onderhouden en te verplaatsen, zelfs als u van plan bent uw bedrijf naar een ander gebouw of een andere locatie te verhuizen. Ook al worden gebouwen opgeknapt en herbouwd, werk blijft onaangetast. U kunt de workflow nog steeds uitvoeren zonder dat u zich zorgen hoeft te maken over bedradings- en verbindingsproblemen. Deze functie kan ook veel tijd besparen, geld, en energie om zich te helpen concentreren op zakelijke en aanverwante taken.
Het nadeel van WiFi
Draadloze LAN-technologie is altijd handig, maar soms moet u misschien rekening houden met de beperkingen van WiFi. Wat zijn die nadelen? Hieronder volgen enkele van de problemen (nadelen) die tegen kunnen komen.
Veiligheidsproblemen
De meeste open WiFi-netwerken zijn onveilig om verbinding mee te maken, omdat niet bekend is wie er op het netwerk is aangesloten. Openbare WiFi-netwerken hebben de neiging te hacken. Hackers kunnen hun ID's nabootsen als netwerk-ID's, wat ook mensen of bedrijven kan kosten. Vandaar, het is het beste om alleen zaken te doen op zakelijke of particuliere netwerken.
Beperkte dekking
Het tweede meest voorkomende nadeel van draadloze LAN's zijn bereikproblemen. Omdat het gebouw een structuur met meerdere verdiepingen heeft. De typische WiFi varieert van 100 tot 150 voeten in een gebouw. Wanneer u zich niet in de buurt van de locatie van het toegangspunt bevindt, het bereik en de sterkte van wifi-apparaten neemt af. Als u zich niet binnen het netwerkbereik bevindt, u kunt geen verbinding maken met het netwerk, die de workflow kunnen verstoren.
interferentie
Wi-Fi-apparaten werken doorgaans op 2.4 GHz en kan worden verstoord of geblokkeerd door andere elektromagnetische apparaten of muren tussen deze apparaten en de WiFi-bron. Dit signaalprobleem kan verbindingsproblemen veroorzaken, of het kan ervoor zorgen dat de signaalsterkte zwak is en langzamer gaat. In dit geval, het overbrengen van grote bestanden via het netwerk is riskant. In dit geval, de gegevens hebben de neiging tijdens het transport beschadigd te raken.
Bandbreedtegebruik
Hoe meer apparaten verbonden zijn met één WiFi-netwerk, hoe zwakker de bandbreedte. Dit is een van de voor de hand liggende nadelen van WiFi op de werkplek. Meer gebruikers betekent beperkte snelheidslimieten en trage workflows.
Langzamer dan LAN
Op het werk of thuis, draadloze LAN's zijn langzamer dan bekabelde netwerken. De meeste draadloze signalen worden gedissipeerd of verspreid door andere apparaten of externe EMF-bronnen. A 2011 Uit onderzoek genaamd “Home WiFi” bleek ook dat WiFi-internetverbindingen mogelijk zijn 30 procent langzamer dan bekabelde.
De gezondheidseffecten van WiFi
WiFi kan schade aan de testis/sperma veroorzaken, en neuropsychiatrische effecten op de menselijke gezondheid, blijkt uit onderzoek dat onlangs is gepubliceerd in Science Direct. Andere gezondheidsrisico's van WiFi zijn onder meer cellulaire DNA-schade, apoptose, calcium, en overbelasting van endocriene veranderingen.
8. Toepassingsvoorbeelden van WIFI-technologie in het Internet of Things
Momenteel, Er zijn veel draadloze WiFi-communicatiemodules voor het Internet of Things op de markt. De Esp32-s3-module kan de fysieke apparaten van gebruikers verbinden met een draadloos WiFi-netwerk voor internet- en LAN-communicatie. De module wordt voornamelijk gebruikt in intelligent transport, slim elektriciteitsnet, industriële controle, slimme woning, draagbare toestellen, en andere velden.
Esp32-s3 integreert 2,4 GHz wifi (802.11b /g/n) en ondersteunt een bandbreedte van 40 MHz; Het energiezuinige Bluetooth-subsysteem ondersteunt Bluetooth Mesh en Bluetooth 5 (DE) en kan over lange afstanden communiceren met gecodeerde PHY en uitzendextensies. Het ondersteunt ook 2Mbps PHY voor een hogere datadoorvoer en transmissiesnelheid. De Wi-Fi- en Bluetooth LE RF-prestaties van de esp32-S3 zijn superieur en werken betrouwbaar bij hoge temperaturen.
Esp32-s3 is een WiFi-module die 2,4GHz Wi-Fi integreert (802.11b /g/ N) en ondersteunt een bandbreedte van 40 MHz. Het ondersteunt gegevensoverdracht tussen seriële poorten en WiFi. De module integreert MAC, radiofrequentie-zendontvanger, basisband verwerking, WiFi-protocol, netwerkprotocolstapel, en configuratie-informatie. Gebruikers kunnen eenvoudig de draadloze netwerkfunctie van seriële poortapparatuur realiseren door deze te gebruiken, zorgen ervoor dat het product sneller op de markt komt.
Traditionele seriële poortapparaten kunnen gegevens overdragen via internet zonder enige configuratie te wijzigen met de ESP32-S3-module. Bieden een snelle oplossing voor seriële apparaten van gebruikers om gegevens via het netwerk over te dragen.
Bij het selecteren van een WiFi-module voor Internet of Things, we moeten aandacht besteden aan de parameters van de WiFi-module: maat, pakket, frequentiebereik, datasnelheid, overdrachtssnelheid, transmissie afstand, communicatie-interface, voedingsspanning, antenne-interface, enz.
Het vooruitzicht van het Internet of Things is groots en verreikend. Nieuwe functies en applicatielagen ontstaan in een eindeloze stroom, en WiFi-modules betreden steeds sneller het veld van het Internet of Things. Feirui technologie-agent Lexin-producten, in het intelligente huis, intelligente medische, intelligente beveiliging, De intelligente industrie en andere gebieden zijn volwassen geworden om klanten onderzoeks-, ontwikkelings- en productieoplossingen voor WiFi-modules te bieden en hebben een positieve reactie van de markt gekregen.
Een paar jaar geleden, Je hebt je misschien afgevraagd hoe dichtbij de landing van het Internet of Things is. Nu, het internet der dingen is overal in ons leven aanwezig. WiFi lijkt meer op een groot netwerk. In het leven, zolang er intelligente eindapparaten worden gebruikt, er zal WiFi zijn.
De beschikbaarheid en populariteit van WiFi is een voordeel dat ongeëvenaard is door andere draadloze technologieprotocollen. Met de ontwikkeling van de slimme huizen, Wi-Fi-modules zullen in de toekomst de hoofdrolspeler worden op het gebied van draadloze interconnectie.
9. WIFI IoT-oplossing
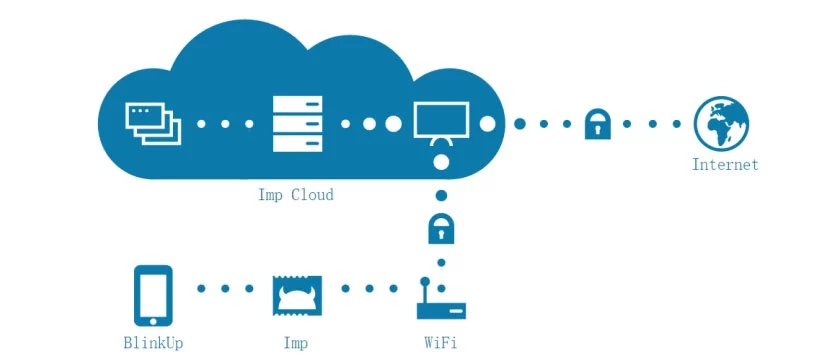
Intelligente thuisoplossing van Internet of Things op basis van WiFi-module
Het Internet of Things is gebaseerd op de onderlinge verbinding tussen objecten, en het is eenvoudig, Stabiele en betrouwbare netwerkmogelijkheden zijn een van de belangrijkste factoren bij de ontwikkeling ervan. Het draadloze internet der dingen is belangrijk vanwege de brede verspreiding van apparaten en objecten die op het netwerk zijn aangesloten en de voordelen van draadloze communicatietechnologie op het gebied van netwerkgemak.
Het tempo van smart home-producten versnelt geleidelijk, en de marktvraag naar draadloze modules zal ook een stijgende trend vertonen. De smart home-oplossing van het Internet of Things op basis van de WiFi-module ondersteunt in principe de thuis- en afstandsbedieningsmodi.
Thuis, hoe maakt WiFi in smart home-producten/-apparaten verbinding met WiFi in thuisrouters? Er zijn twee manieren om APP te verbinden (SmartLink smart home-modus) en AT-instructieset.
SmartLink is een intelligente netwerktechnologie die WiFi-modules verbindt met draadloze routers. De SSID en het wachtwoord worden gecodeerd met broadcastpakketten en verzonden via broadcastpakketten.
UDP kan broadcastpakketten op de applicatielaag verzenden. Vandaar, het pc-programma of de APP verzendt een UDP-pakket en plaatst de SSID en het wachtwoord in het pakket. Na ontvangst van het pakket, het intelligente apparaat parseert het pakket om de SSID en het wachtwoord te verkrijgen en kan de router configureren en er verbinding mee maken.
De bloeiende toepassing van het Internet of Things heeft ook een nieuwe reeks zakelijke kansen op het gebied van draadloze communicatietechnologie met zich meegebracht. Steeds meer chipmakers (zoals processors en microcontroller MCUS) proberen de ontwikkeling van WiFi/BT/ZigBee-technologieën te versnellen om de IoT-markt aan te boren.
Producten en oplossingen zoals geïntegreerde draadloze single-chip MCU, geïntegreerde MCU en draadloze functiemodules, geïntegreerde embedded processors en draadloze single-core SOC zijn op een alomvattende manier tot bloei gekomen.
WiFi-module behoort tot de transmissielaag van het Internet of Things. De seriële poort of TTL-niveau wordt omgezet in een ingebedde module die voldoet aan de Wi-Fi draadloze netwerkcommunicatiestandaard en de IEE802.11 protocolstack-netwerkstandaard. De ingebouwde TCP/IP-protocolstack kan elke transparante conversie realiseren. Zorg ervoor dat traditionele seriële apparaten beter verbinding kunnen maken met het draadloze netwerk.
10. De geschiedenis van WIFI
In het verleden 20 jaren, met de snelle ontwikkeling van WiFi-technologie, onze mobiele telefoons, laptops, iPads en andere draadloze netwerken kunnen met hoge snelheid toegang krijgen tot internet, wat onze manier van leven enorm heeft veranderd en een essentieel onderdeel van ons leven is geworden
In de jaren 1990, IEEE heeft een speciaal 802.11 groep om WLAN te bestuderen en aan te passen(Wireless Local Area Network) protocollen en specificaties, en lanceerde vervolgens verschillende generaties WiFi-protocollen
1. In 1997, de 80.11 groep introduceerde de 802.11 protocol. WLAN was oorspronkelijk alleen in de 2,4GHz-band met een maximale snelheid van 2 Mbps
2. 802.11er werd een protocol geïntroduceerd 1999. Om de snelheid van draadloze transmissie te verbeteren, WLAN werkt in de 5GHz-band (enkele band), met de hoogste transmissiesnelheid 54 Mbps. In hetzelfde jaar, 802.11b werd geïntroduceerd voor 2,4 GHz WLAN, waardoor de maximale snelheid van 2,4 GHz werd verhoogd naar 11 Mbps
Tegelijkertijd, een andere belangrijke gebeurtenis was de oprichting van de Wi-Fi Alliance dit jaar, de officiële geboorte van het woord WiFi
3. In 2003, 802.11g-protocol en OFDM-technologie werden geïntroduceerd. 802.11g is het eerste dual-band WiFi-protocol, ondersteunt zowel 2,4 GHz als 5 GHz, erft de hoogste transmissiesnelheid van 54 Mbps van de 2,4 GHz-band van 802.11b en de 5G-band van 802.11a. Het is ook achterwaarts compatibel
OFDM (Orthogonale frequentieverdeling Multiplexing) technologie, is van MCM (Modulatie met meerdere dragers, Multicarrier-modulatie (ontwikkeld vanuit een lage implementatiecomplexiteit, het meest gebruikte multicarrier-transmissieschema
4. Geïntroduceerd 802.11n-protocol in 2009. Nieuwe technologieën omvatten MIMO, MCS en Beamforming
802.11n voegt MIMO-technologie toe en ondersteunt een bandbreedte van 40 MHz, met snelheden tot 600 Mbit/s bij gebruik van 40 MHz bandbreedte en 4*4 MIMO
5. 802.11AC gelanceerd (Wifi 5) protocol en MU-MIMO-technologie in 2013
Wifi 5 protocol 5GHz-band enkele antenne maximale snelheid van 866Mbps, 8*8 MIMO (8T8R) theoretisch tarief van 6.9 Gbps. Terwijl 802.11AC goede achterwaartse compatibiliteit biedt, de bandbreedte van 5GHz wordt vergroot tot 80MHz (de hoogste is 160 MHz, maar de chipfabrikant implementeerde slechts een bandbreedte van 80 MHz; Wifi 6 werd op grote schaal gecommercialiseerd tot een bandbreedte van 160 MHz), en de modulatiemodus is geüpgraded van 64-QAM naar 256-QAM.
In 2019, 802.11bijl (Wifi 6) protocol, OFDMA-technologie en MU-MIMO-upgrade
Wifi 6 enkele stroom (1T1R) tot 1200 Mbps, (8T8R) tot 9,6 Gbps, heeft hoofdzakelijk de volgende kenmerken:
Lage latentie (MU-MIMO-technologie en OFDMA-ondersteuning)
Laag energieverbruik (TWT-technologie, voornamelijk weerspiegeld in de optimalisatie van het slaap-waakbeheer van IoT-apparaten)
Hoge snelheid (MU-MIMO, coderingsmodus geüpgraded van 256-QAM naar 1024-QAM)
11. Veelgestelde vragen over WiFi Internet of Things
Zijn WiFi-golven schadelijk??
Draadloze routers zenden elektromagnetische straling uit op lage gigahertz-frequenties. Dit niveau is gevaarlijk voor mensen. Langdurige blootstelling aan elektromagnetische frequenties kan schadelijk zijn voor de gezondheid.
Wat zijn de belangrijkste beperkingen van WiFi?
WiFi heeft de mogelijkheid om WiFi-signalen te gebruiken binnen een 100 – tot een limiet van 150 voet, fysiologische interferentie veroorzaakt door andere elektronica, en relatief lage bandbreedte wanneer meerdere gebruikers zijn aangesloten.
Is WiFi slecht voor je gezondheid??
Sommige onderzoeken hebben aangetoond dat wifi DNA-schade veroorzaakt, endocriene veranderingen, apoptose en oxidatieve stress, aangezien een aantal onderzoeken en onderzoeken de potentiële risico's van blootstelling aan wifi blijven onderzoeken.
Veroorzaakt WiFi kanker??
Er is geen sterk bewijs dat het antwoord uitdagend maakt. Er is geen medisch of klinisch bewijs om dit te ondersteunen, hoewel er in de media wordt gespeculeerd dat wifi kanker kan veroorzaken. Wi-Fi verzendt informatie zoals mobiele telefoons w
















