どのような業界なのかを詳しく紹介します 4.0 は, 産業の発展の歴史 4.0, それが私たちの製造業にもたらす変化, 仕事の利点 4.0, 遭遇するであろう課題, そして世界のトップ産業 4.0 企業. ついに, よくある質問にお答えします. この記事を通じてより完全に理解できるようになります.
産業とは 4.0 参照する?

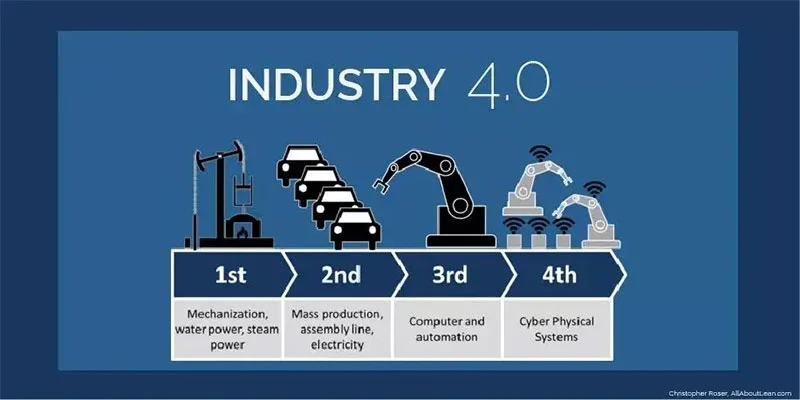
いわゆる産業 4.0 産業発展のさまざまな段階の区分です. 業界 1.0 蒸気機関の時代です, 業界 2.0 電動化の時代です, 業界 3.0 情報技術の時代です, そして業界 4.0 を使う年齢です 情報技術 産業変革を促進する, あれは, 知性の時代.
で 2013, このコンセプトはドイツで初めて登場し、ハノーバー メッセで正式に発表されました。. その中心的な目的は、ドイツの産業の競争力を促進し、産業革命の新ラウンドを主導することです。.
その後, それは、ドイツ政府によって提案された 10 の将来プロジェクトの 1 つとして含まれていました。 2020 ハイテク戦略. 製造業の知能レベルを向上させ、資源効率の高いスマートファクトリーの構築を目指すプロジェクト, 適応力, そして遺伝子工学. モノのインターネットとネットワーク エンティティ システムはその技術的基盤を構成します.
産業の歴史 4.0
履歴行
産業の概念 4.0 ドイツに来て 2011. ”業界 4.0中小企業の有識者によるワーキンググループを設置, 関連するドイツの業界団体, 政府, 研究機関, そして大学, それ以来、ドイツおよび世界中で関連する工業化に関する研究をさらに実施してきました。. 作業部会は4月に最終報告書「ドイツ製造業の将来の確保」を提出した。 2013: 「産業」の実現に向けた提言 4.0 「ドイツ連邦政府に対する戦略」. さらに, 業界 4.0 ドイツ連邦政府がその後立ち上げた「ハイテク戦略2020」の将来の10プロジェクトに含まれている, こうして産業が生まれる 4.0 国家戦略上重要な.
基本的な考え方
業界 4.0 ハイテク分野における革新的なアイデアを世界に紹介するドイツ初の大規模な試み. 「インダストリー 4.0」により、ドイツの化学分野の生産額が増加すると予想されています, 工業製造業, 農業, 自動車, とITによる 78.7 10億ユーロ, ドイツ全体の生産額を増加させる 267 までに10億ユーロ 2025. あたりまでに 2030, ドイツの生産性はさらに上昇すると予想される 30 に 300 パーセント.
このアイデアは、いわゆる「ネットワーク物理生産システム」で仮想空間と物理空間をリンクし、デジタルの進歩を活用して次世代の工場を構築することです。. ドイツはパーソナライズされた製品の品質確保を重視し、より効率的な生産をベースにパーソナライズされた製品と高付加価値の両立を追求しています。.
戦略的意図
ドイツは一方で、インテリジェント技術による生産の自動化を切実に必要としている。倉庫保管や輸送などの生産的なサービスへの移行が必須, 市場分析とマーケティング, エネルギー貯蔵, そして製品テスト, 高品質な生産を維持するために。
ドイツは、新技術が伝統産業に力を与え、新たな世界的な「インターネット時代」の優位性を競うことを期待している。. ドイツは経済規模の限界により、インターネット時代には中国や米国に大きく後れを取っている. 電子商取引, それ, ソーシャルネットワーク, サーチエンジン, インターネットに基づく一連のビジネス モデルのイノベーションは、最初に米国で考案されました。. ドイツができるのは、製造業における技術的優位性を最大限に発揮し、産業用インターネットと家庭用モノのインターネットの開発に注力することだけです。. 以来、 2008 経済危機, 先進国の市場需要は低迷している. 供給側では, 中国およびその他の新興国, 巨大な国内市場に依存している, 製品の新しいテクノロジーを常にアップグレードし、反復しています.
業界のメリット・メリット 4.0

業界の特徴 4.0 とても明確です, つまり, 情報通信技術とサイバー空間仮想システムの融合による製造業のインテリジェンス化. この変更のもとで, 「インテリジェントなものづくり」をテーマに, 産業における「インテリジェント生産」と「インテリジェント物流」 4.0 企業は高度に自動化されます, 非常に有益な, 高度にネットワーク化された, これは、企業の設備に対する関心を大幅に高めるだけでなく、業界における設備管理に対する新たな要件も提起することになるでしょう。 4.0 環境.
業界 4.0 三重の利便性をもたらします
業界 4.0 設備管理に大きな影響を与える. インターネットを介して工場の垂直統合とエンドツーエンド統合が完了した後, 工場全体または複数の工場の設備が相互接続されたネットワークを形成します, システムは自動的にすべての人員を動員して機器のメンテナンスを実行します。. 管理者は、すべての設備のリアルタイムのステータスに従って生産計画と構成を実行できます。, 機器のメンテナンス経験や障害情報をより完全に共有し、伝達できるようになります。, 機器のスペアパーツをより適切に調整して管理および使用できるようになります。, 機器の使用効率と高速応答速度が大幅に向上します。. 具体的には, それは主に次の3つの「便利さ」に反映されます。.
テクノロジーおよびネットワーク指向の産業向け 4.0 業界の変革, 最初に考えられる打開策は、機器管理の現在の組織構造です。.
現場の人々のモチベーションを高めるという点でもひどい仕事をしている. しかし, 無駄のない生産を導入している多くの企業で, トータルな生産的メンテナンス (TPM) リニアユニティ形式の欠点を部分的に補う機器管理システムのベースの方法, それは、問題を解決するためのグループの活動からの団結のマトリックス組織構造システムを外側に直線的に増加させます, さまざまな部門のメンバーが定期的にチーム活動を行い、コミュニケーションを図ります。, 情報伝達が増えた, レベル間の情報共有が大幅に改善されました. しかし, このようにして, マネージャーと草の根スタッフは依然として結果重視のボトムアップ報告プロセスを行っています, 一方、活動グループは上級マネージャーから情報を得るプロセスにおいて比較的受動的です。.
情報共有の問題は業界では当然のことです 4.0 企業, 業務端末から直接情報収集・分析が可能 (デバイス) モノのインターネットを通じて. 関連する許可が開かれている限り, すべての情報はデータベースの検索端末を介して取得できます. 統一されたシステムで, すべてのデータを繰り返し収集する必要はありません, 呼び出して継続的に計算するだけ. 例えば, 生産現場で, 設備総合効率データ (OEE) 本来は、装置の計画された生産プロセスの実際のダウンタイムを収集するために必要です, 各パートの制作テンポ, 生産された部品の数, 一定期間内の認定製品の数. 一般的に, これらのデータは、さまざまな機能部門のさまざまなシステムから取得される可能性があります。, しかし、の時代に 4.0, これは高度に情報化され、ネットワーク化されています, すべての情報は、機器からリアルタイムで取得できます (問題は、インテリジェントファクトリーの情報に等しくなります), また、フィードバックの結果はリアルタイムで計算できます.
情報とネットワーキングの利便性のため, 多くのプロセスと作業はコンピューターによって実現されます. 高度な自動化を備えています, 工場の元の労働集約型の生産フォームは、徐々に資本と技術集約型の形に変更されました, そして、この変化は、中国のより発達した沿岸地域でますます明白になっています, 中央および西部地域に徐々に広がっている間. 効率的な情報処理とインテリジェントな意思決定の助けを借りて, すべての管理範囲が大幅に増加します. この変更により、管理体制がより平坦になり、組織の情報がより完全に共有されるようになります。.
設備管理プロセスは劇的に変化し、実行はより標準化されました
工場情報とネットワークの充実により, 設備の自動化度も同様, 設備管理システムのプロセスが大きく変わる. これまで人間が行っていた作業の多くは、機器によって置き換えられることになります。, そして、数年前に銀行員がコンピューターやATMに取って代わられたシナリオは、工場でもより頻繁に起こるだろう。.
業界 4.0 設備管理システムの構築に役立ちます. 十分で効果的なデータは、システム構築の初期段階で意思決定者の基礎を提供できます。, 効果的な分析システムにより、システム構築の効率と効果が大幅に向上します。. 例えば, 設備の総合効率を向上させる, このシステムは、意思決定者が設定されたパラメーターに従って関連データを自動的に収集するのに役立ちます。, データの総合的な効率に影響を与える重要な要素を見つけます, より効率的かつ適切に問題を研究し解決するため.
この変更は、機器管理システムの導入にプラスとなります。, そして、人的要素がより多く含まれた元の実装プロセスは、より標準的かつ厳格になります。. システムはシステムやプロセスに合わせて手順を設定するだけ, そして条件が揃ったとき, それらは厳格に実施されるだろう, 手順も明確になります. 例えば, 機器故障報告システム, プロセスの文書化には、さまざまなダウンタイム期間の後にさまざまなレベルの対応が必要です. 情報化が不十分な状況下で, 時機を逸した情報伝達と人為的な隠蔽は、バックパッシングと時機を逸した対応を引き起こす.
しかし, 産業の工場で 4.0, システムは、さまざまな時点でさまざまなマネージャーに情報を自動的に送信します。: 設備が故障したら, システムはすぐにチームリーダーに通知します; 機器が期限内に回復しない場合 15 分, システムは自動的に保守担当者に修理するよう警告します。; 後で機器が修理できなかった場合 1 時間, システムはワークショップディレクターにアップグレードされます. プロセス全体を通して, 機器は設定されたメンテナンス計画に厳密に従って自動的にガイダンスとアラームを発行し、関連する実装者にタスクを完了するよう思い出させます。. システム主導の導入プロセスにおいて, 実装者にはいかなる言い訳も許されない, そしてすべての職員は厳格に標準化された労働状態に引き込まれます。.
素材はデータです, 機器のメンテナンスがより便利になります
業界 4.0 素材はデータであることを強調する. 技術的には, 機器の完全なセットであっても、機器のコンポーネントであっても, 理論的には関連情報をシステムに提供できます. 事前に収集されたデータを使用して、潜在的な障害を警告できます。, 障害に近い状態や破壊的な現象に対処する必要がなくなる. 例えば: ベアリングの振動周波数と元のデータからベアリングが損傷しているかどうかを判断します. 周波数変化が見つかった場合, ベアリングは急速な損傷を受けることがよくあります, 機器の効率に大きな影響を与える. 産業下のインテリジェントベアリングですが、 4.0 原材料とベアリンググリースで対応するセンサーを増やすことができます. 軸受の素材の応力がある程度変化したり、軸受グリース中の金属片の濃度が一定値に達した場合, メンテナンスまたは修理情報はシステムを通じて送信されます, 準備とメンテナンスの時間が大幅に早まるため、.
業界の課題 4.0.
業界の課題 4.0

ドイツは産業の概念とビジョンを提唱しましたが、 4.0 できるだけ早く 2011, その後の結果 10 何年も期待された目標を達成できませんでした. 10月中 2019, いくつかのシンクタンク, DIWベルリンを含む, イフォ, IfW キール, RWIとIWH, 「ドイツ経済は停滞に直面している」と題するレポートを共同で発表, レポート, ドイツの製造業の急速な悪化を挙げた。, ヨーロッパ最大の経済大国, ユーロ圏衰退の主な原因として.
中小企業が業界の受け入れに最も困難を抱えている 4.0
ドイツ政府はドイツ人を発表した。 AI 人工知能製品の開発と応用、および分野全体の産業変革を促進する開発戦略 2018. ドイツのアルトマイヤー経済・エネルギー大臣も、この政策の目標は産業を完全にカバーすることであると述べた。 4.0 テクノロジー. 対照的に、, 産業のより一貫した使用 4.0 中小企業はさらに別のものを追加できる 0.3% ドイツのGDP成長率に貢献.
一方で, 業界 4.0 データセキュリティの懸念が最大の「ネック」となる. このエコシステムでは, 企業は新たなシステム依存性を持つだけでなく、新たな形式の攻撃手段も持つ必要がある, これにより、情報セキュリティが大きな弱点にさらされることになります. 技術的および財政的問題により制限される, 中小企業はデータ漏洩の可能性が高い, 一度漏洩すると修復できない. ネットワークのセキュリティ上の不安も知的財産の漏洩を引き起こす可能性があります. デジタル化がもたらすリスクをあまりにも低く見積もる企業が増えている. 多くの企業は、生成したデータを保護できないと感じているため、ビッグデータを完全に活用することに消極的です。.
専門的な才能の欠如が最大の欠点です
30% のドイツ企業が産業界の人材需要を倍増させた 4.0. で 2019. 実は, 巴州が割り当てを発表 4 建設に100万ユーロ 12 デジタルトランスフォーメーションによる労働需要の変化に対応するため、専門学校や専門学校で「ラーニングファクトリー4.0」を4月初旬から導入 2015. 目的は、研究費を増やすことです。 3.5 GDPのパーセント 2025, 将来に必要なIT人材と熟練したネットワークエンジニアの育成に注力.
世界的に「インダストリー4.0」の推進が顕著になる
各国の産業用インターネットのリファレンス アーキテクチャには大きな違いがあります, 世界的な推進の過程で「インダストリー4.0」の異質な傾向がますます顕在化.
初め, 名前の表現と開発への焦点は同じではありません. 日本は「インターネット産業」と呼ばれています, 中国で, 「インダストリアルインターネット」と「スマート製造" 使用されています, 米国は「インダストリアル・インターネット」と呼ばれています. 名前の違いは、各国が独自の産業用インターネット標準を確立したいことを示しています, 自社の知的生産技術の世界的普及を推進するため, システムソリューション, 独自の産業上の優位性を強化しながら、. その間, 主要先進国では、産業用インターネットのリファレンス アーキテクチャの重点に多くの違いがある, これは、各国の産業および製造業の発展の状況と目標の違いを反映しています。. ドイツの「インダストリー 4.0」リファレンス アーキテクチャは機器を重視; 日本の産業バリューチェーン参照フレームワークは接続性を重視; 中国は新世代の情報技術と製造業の緊密な統合を重視.
2番, この分野で, 国が違えばメリットも違う. 企業や地域の発展レベルは非常に不均一です, そして産業条件の違い, 開発コンセプト, そして利点は、いくつかの国がこの分野に独自の機能を持っていることを決定します.
三番目, ドイツの経済規模は、グローバリゼーションにおける「Industry4.0」の実施に大きな利益をもたらさない. 例えば, 中国の経済規模はドイツの経済規模とは異なります, そして、中国の開発パスは、ドイツの経験を「コピー」することは不可能であると判断します. 業界 4.0 ドイツの国家状況によって提案されている概念です. 一方では, ドイツは長い間製造業に基づいています. 一方で, ドイツは、短く単一の産業チェーンを備えた小さな国です. 中国と米国は巨大な単一経済です, だから私たちは経済全体の運営について考える必要があります. 現在のところ, 中国の産業グレードの世代のギャップは大きいです, そして、いくつかの産業は先進国のレベルに達しました, しかし、業界を包括的に促進することにも大きな問題があります 4.0.
産業はどうなるのか 4.0 製造業を変える?
で 2025, 拡張現実市場とグローバルな仮想現実に到達する $80 十億. アプリケーションシナリオは医療です, 不動産, エンジニアリング, また、他の重い資産産業が不可欠です. 多くの人々は、おそらく最初に、現実の拡張に関して一晩で世界を嵐に巻き込んだポケモンARゲームを見ています. 実は, 拡張現実であろうと複合現実であろうと, これらの技術は、工業製造の分野にも適用されています.
1. 工業デザイン
伝統的な工業デザインの段階は構成されています 5 主な手順: 顧客の要件を理解する, 要件をテクノロジー入力に変換します, 複数のソリューションを提供します, 顧客に受け入れられる実行可能なソリューションの選択と、確認されたソリューションを製造チームに転送する. 別の言葉で, この従来の設計プロセスには、クライアント企業に最適な実行可能な製品を決定するために多くの労力と時間が必要です. 拡張現実を開発と設計の段階に統合することで、伝統的に退屈なプロセスを簡素化できます, 顧客とのやり取りを改善します.
エンジニアは、車内の構造情報を見ることができます, 特定の部品の3Dグラフィックスも同様です, それらを調整します. また、営業チームやデザイナーと迅速に通信することもできます, 消費者需要の好みを完全に理解しています, 新しい車の速度を向上させますr&D開発.
2. 組立と製造
多くのリンクには、工業生産プロセスにおける労働者の手動操作も必要です. アセンブリサイクル時間はオペレーターのスキルによって異なります, 特に航空機で, 車, その他の複雑な大きな機械装置. 例えば, 航空機には、大量の複雑な数の電子回路があります, アセンブリエンジニアは、何千ものワイヤーを備えたワイヤーハーネスアセンブリの機能マニュアルに従う必要があります, 時間と時間のようなプロセス. 航空機メーカーのボーイングはARメガネを使用してGoogleのアセンブリプロセスを簡素化します, APX Labsを介してアプリケーションを開発しました, エンジニアは、アセンブリコンポーネントのシーンをスキャンするQRコードをARレンズできます, ワイヤーハーネスアセンブリ命令のコンポーネントは、メガネに自動的に表示されます, あなたは議会労働者を完了するための指示手順に従って必要です.
エンジニアの組み立て時間は短縮されます 25% エラー率は減少します 50% 統計に従って. ロッキード・マーティン, アメリカの軍用機の最大のメーカー, ARを航空機の製造プロセスに組み込もうとしています. 同社は、生産スタッフが操作プロセスと部品の数を簡単に知ることができるようにすることができます, したがって、Epson MoverioのARメガネの助けを借りて、迅速かつ正確な組み立て生産を可能にします. 着陸装置コンポーネントをインストールするとき, エンジニアは、ARメガネに表示される設置マニュアルと手順を使用してケーブルについて学ぶことができます, ボルト, インストール位置, およびシリアル番号.
3. 品質検査
品質検査は、製品がすべての要件を満たすことを保証するための不可欠なステップです. 従来の制作には、チェックポイントの広範なチェックリストが必要です, 品質検査官は最終製品の納品に責任を負います. したがって、, 顧客が受け取る製品の品質は、製品の品質管理と品質検査プロセスの精度に影響されます。. AR技術により公差などの詳細情報を閲覧可能, 寸法精度, 表面仕上げをリアルタイムに表示, QC担当者が複雑なタスクを簡単に実行できるようになります.
マグナは、Microsoft HoloLens を使用して部品や車の潜在的な欠陥の検査を支援しています. AR メガネは、ホロレンズを装着した検査員が車を見ると、検査対象の部品に関する情報を表示し、検査員をガイドします。.
拡張現実は、ライプツィヒのポルシェ組立工場で品質保証プロセスのツールとして技術者によって使用されました, ドイツ. QCの担当者はARデバイスを使用して、車の問題部分の写真を撮ります, そして、パーツの正確なサイズを自動的にロードします. 質の高い検査官のために多くの時間が節約されます.
Mixed RealityアプリケーションMIRAは、エアバスが生産中にデジタルモデルを統合するために使用されます. A350 XWBおよびA380の生産ラインには、二次構造サポートの完全性を確認するために、Mixed Reality Technologyが採用されています。.
4. メンテナンスとアフターサービス
さまざまな機器の定期的なメンテナンスは、毎日の生産の通常の運用を確認するためにすべての業界に必要です, しかし、製造業の関連する機器のメンテナンスははるかに複雑です. 機器の機能と構造に完全に精通する必要があり、サービスマニュアルの何百ページも参照する必要があるため.
メンテナンス担当者は、タブレットの機器の問題を確認することができます, ARメガネは会社によって開発されたARアプリを介して開発されました. メンテナンス作業は、インタラクティブな視覚操作を介して完了することもできます.
5. 従業員研修
企業は、従業員の安定性とスキルを向上させるために、さまざまなトレーニング活動に多くのお金と時間を投資することがよくあります. ARテクノロジーにより、トレーニング方法がインタラクティブになります. ブレークスルー位置の制限とトレーニング中の従業員の安全性を確認する.
Automotive Technology Provider Boschは、従業員のマニュアルをデジタル化する拡張現実アプリを開発しました, トレーニング計画, 画像を提供する他のコンテンツ, アニメーション, 文章, オーディオ, ビデオ, もっと. 技術者はダッシュボードにiPadをポイントして、新しく設計されたアプリでデバイスの後ろに隠されているすべてを見ることができます. 技術者は、さまざまな配線の正確な位置を簡単に決定し、センサーを使用して各コンポーネントと対話することができます. このプログラムは、配線図と接続を生成します, コーチが時間を費やすことなく実際の車両でトレーニングエクササイズを行うことを可能にすることを可能にします。.
]JLRは、最小限のトレーニングコストで新入社員の迅速なトレーニングを達成しました. 拡張現実は、テクノロジーが成熟し、コストがさらに下がるにつれて、製造により多くの変化をもたらします, デジタルツインニングとの統合だけでなく, 産業用モノのインターネット, 3D印刷, 予測分析, 機械学習, およびその他のテクノロジー.
トップ業界 4.0 企業
1. アンバーグのシーメンス スマート ファクトリー, ドイツ
Siemens AGは、に設立された電子および電気工学のグローバルリーダーです 1847. 7月 19, 2018, シーメンスはフォーチュングローバルで66位にランクされました 500 リスト.
ニュルンベルクで, バイエルン州東部の小さな都市, 控えめな工場があります, しかし、誰がそれがヨーロッパと世界で最も先進的なものの1つになると思っていただろう?
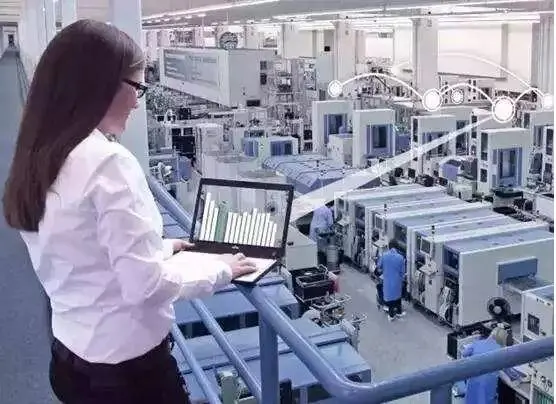

いくつかのデータを通して工場を見てみましょう:
24-時間配達時間
1秒ごとに1つの製品
パスの割合はです 99.9985%
管理 3 10億コンポーネント
について 1200 従業員
5 kmコンポーネント用の地下輸送ベルト
磁気浮揚ベルト
工場, 生産機器, コンピューターは処理できます 75 仕事自体の割合, 手動で行うために作業の4分の1だけを残す
- これはシーメンスアンバーグ工場です!
これはシーメンスの未来の工場です, 産業の最も代表的なもの 4.0, Amberg Electronics Manufacturing Plant (ドイツの略語: EWA), 世界初の純粋なデジタル工場.
構築されたので, 工場の生産エリアは拡大しておらず、従業員の数はほとんど変更されていません, しかし、その能力は8倍に増加しました, 平均して1秒あたり1つの製品に. その間, 製品品質の適格なレートは 99.9985%, そして、世界の同様の工場は一致しません.
2. ボッシュ フンボルト工場(ドイツ)
ボッシュは、スマートトランスポーテーションテクノロジーに従事するドイツの産業企業の1つです, スマート産業技術, ビルディングテクノロジー, エネルギー, 消費財。
ボッシュは雇用しています 230,000 以上の人々 50 国とそのシステムソリューションと最先端の製品でよく知られています.
○n 7月 19, 2018, ボッシュグループはノーにランクされました. 75 フォーチュングローバル 500 リスト。
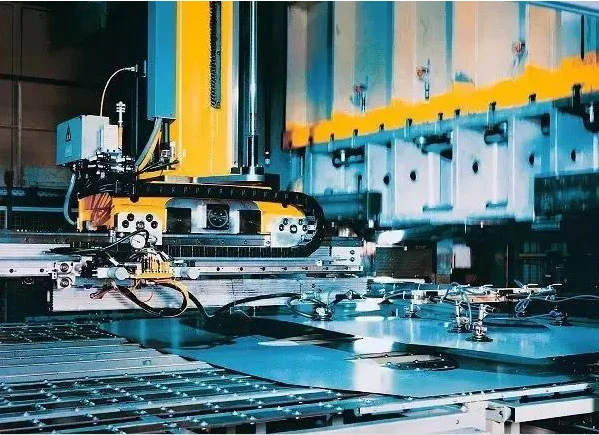

世界のナンバーワンの自動車技術サプライヤーとして, ボッシュの自動車ブレーキシステム (腹筋&特に) 市場でかなりの強みがあります. ボッシュフンボルト工場, ボッシュのスマート工場の代表, 生産ラインに特別な機能があります: すべての部品にはユニークなものがあります RFID 途中でチェックポイントに自動的に「話し合う」番号. 各生産リンクの後, カードリーダーは、関連情報を自動的に読み取ります, 対応する処理のためのコントロールセンターへのフィードバック, 生産効率全体を改善するために.
インテリジェントファクトリーは、手動操作を単に機械に置き換えるわけではありません, しかし、もっと重要なことは, 徐々に知性を導入します, 情報, オートメーション, 製造プロセスをより透明にするために、その他の関連技術, 各製品にスマートIDカードを人身売買します, さまざまな地域で生産された部品をシームレスに作成します.
フンボルトロジスティクスセンターで, ワーカーは、部品の箱が引き出されるたびに製品情報を含む「スラット」を長方形のプラスチッククリップにクリップする. クリップはボックスに取り付けられています, クリップの下部には、無線周波数識別番号があります。パーツボックスのID. 各生産リンクの後, カードリーダーは、関連情報を自動的に読み取ります, 対応する処理のためのコントロールセンターへのフィードバック. 例えば, トラックが物流センターからそれを引き出したとき, 組立工場 5,000 数メートル離れたところに何が起こっているのかがわかります: 組み立て労働者がそれを生産ラインに置く前に, ロジスティクスセンターとサプライヤーは、補充する時が来たことを知っています.
3. BASFケミカルグループのカイザースラウテルン工場
ドイツの化学会社として, BASFは、世界最大の化学工場の1つです.
終わりがあります 160 BASFが運営する合弁事業と完全な子会社 41 ヨーロッパの国, 北アメリカと南アメリカ, そしてアジア. 同社は、ライン川のルートヴィヒシャーフェンに本社を置いています.
7月 19, 2018, BASFは112位でした フォーチュングローバル 500 リスト.

または、無線周波数コードを使用するため, 伝統的な化学大手のBASFはこれをさらに一歩進めています. KaiserslauternのBASFのパイロットスマートファクトリーで製造されたシャンプーおよびハンドサニタイザーは、すでに完全に自動化されています. テスト注文はオンラインで配置されているため, その生産ライン上の手の消毒剤の空のボトルに取り付けられたRFIDタグは、機械と自動的に通信して、どんな石鹸を伝えますか, 香り, キャップカラー, 必要なラベル.
このような組立ラインに, ハンドサニタイザーの各ボトルは、コンベアベルトの次のボトルとはまったく異なる場合があります. この実験は、ワイヤレスネットワークに依存しています, マシンと製品の間のすべての通信が行われる場所, 必要な唯一の人間の入力は、サンプル注文を配置することです. それは実験です, しかし、顧客から工場に直接注文するという考えは、スマートファクトリーモデルに別の開発方法を与えるのに十分です.
業界のよくある質問 4.0
私. デジタル化
デジタルも呼ばれます, 2つの概念には一定の区別がありますが, ここでデジタルの古い資産の必要性はエンタープライズを指します, 組み込みシステムを接続するための生産技術 インテリジェントプロダクション プロセスとエンドツーエンドのデジタル製造プロセス, 製品品質のリアルタイム追跡, 質の低いコストを削減します (copq) 顧客の革新に基づく実装.
企業のデジタル化によってのみ、ロボットやIoTなどのインテリジェントな製造技術を実現できます.
2. テクノロジーのアップグレードと変革
業界のアップグレードと変革を実現するために 4.0, テクノロジーも習得する必要があります, 特にデータ分析と3D印刷. 前者は、デジタル企業を分析することです, 後者をCNC工作機械と組み合わせて、多層製造の革新をサポートできます.
一度霜 & サリバンは、これらの技術が従来の動作モデルを排除すると予測しました, リアクティブメンテナンスから予測メンテナンスへの移行 (PM), 新しいビジネスモデルをサポートします. 特定の商品の販売から「サービスとしてのパフォーマンス」の販売まで.
3. サプライチェーンの運営
製造用, 企業は、上流と下流に協力します, 上流と下流, サプライチェーンの形成, サプライチェーンの操作の安定性を維持することも産業です 4.0 問題に注意を払わなければなりません, かつて日本の地震と津波が電子市場の混乱につながったからです, インテリジェントな時代の生産効率が向上します, その場合、この効果はサプライチェーンのさらに深刻な問題になります.
4. サイバーセキュリティ
業界を構築するにつれて 4.0 デジタル企業とモノのインターネットを通じて企業, ネットワークセキュリティが大きな問題になります. 私たちはネットワークセキュリティを重視し、自分の利益を保護しなければなりません. 例えば, IT/運用技術を設定できます (OT) セキュリティを保護するためのコー.
5. システム
その後、業界に参入する企業 4.0, 製品を変換およびアップグレードするためのテクノロジーに加えて, また、過去のエンタープライズシステムについても考える必要があります, 多くの場合、従来の企業のシステムはスマート企業には適していません, システムも改革しなければならないからです, 特に組織文化, ビジネスリーダーと投資収益率 (ROI) 概念はそうです 4.0 業界には多くの側面が含まれます.
6. 人材育成
業界の才能 4.0 伝統的な企業の議会ライン労働者ではなくなり、オペレーターのスキルに高い要件があります. したがって, 企業は、人材トレーニングにも注意を払う必要があります, 産業に適した技術スキルのための合理的なトレーニングメカニズムを提供する 4.0 全国レベルでは、中国が産業4.0を達成するのにも役立ちます。
















