Nowadays mobile communication network is essential everywhere, it provides us with unlimited convenience, and one of the main positions in the mobile communication network is GPRS, what exactly is this GPRS? Please find more detailed information below.
What is GPRS?

GPRS, namely General Packet Radio Service Technology, is a data service for GSM users.
As a continuation of GSM, GPRS transmits data in the way of packets, which is unlike the previous method of continuous transmission over channels and leads to the cost to the user being calculated based on the unit of data transmitted.
2. How Does GPRS Technology Work?
GPRS works mainly through an internal router for the basic addressing of data or voice signals and for the establishment of normal data connections. Under the management of the router, the mobile terminal will set up the route for sending data, receiving data and those data in roaming conditions.
Routing Set-up for Sending Data
When the mobile terminal establishes the route for sending data, it will generate a PDU (Packet Data Unit) on the terminal, and this PDU will be transmitted through our SNDC data unit, and then be transformed into an LLC frame through the processing of the LLC layer, and eventually entering the basic network SGSN, where the terminal of GSM is located. The SGSN further transmits all the information to the GGSN, which then processes the data and then sends it to the users of our data network to meet their requirements. At the same time, to comprehensively protect the data information, we will encrypt the data of the air interface during the transmission.
Routing Set-up for Receiving Data
When users of our public data network receive the data sent by the previous mobile terminal, they will first establish a route between the data network and GGSN through the standard protocol of our data network for later data transmission. When the data network users send the data unit, the data unit PDU will be transmitted to the GGSN by the established route. Upon receiving the data unit, GGSN will transmit the PDU to the SGSN, which is located with the mobile terminal, and afterward, the GGSN will pack the PDU that arrives and change it into the SNDC data unit for transmission, and then transform it into LLC frame unit after the processing by LLC, and finally transmit the data to the mobile terminal through the air interface.
Routing Set-up for Data in Roaming Condition
The establishment of the data route in roaming conditions needs the help of the GGSN of its home place before it can be transmitted to the terminal of the mobile user. The process is similar to the establishment of the route for transmitting data and the route for receiving data, except that in the end they both undergo frame conversion in the GGSN of the home place to reach the final destination address.
3. The Architecture of GPRS Networks
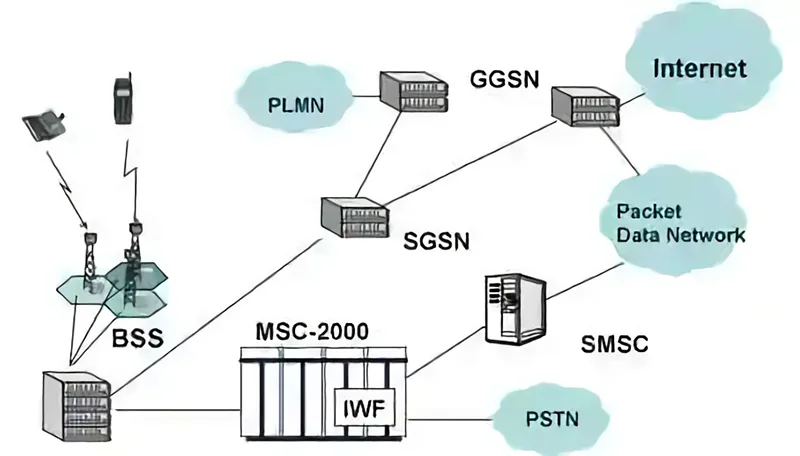
GPRS network is based on the existing GSM network to implement packet data service. GSM is designed for circuit switching, but the existing GSM network is not sufficient to support packet data routing. Therefore, GPRS must add new network instances based on the existing GSM network, such as GGSN (Gateway GPRS Supporting Node), SGSN (Serving GSN) and PCU (Packet Control Unit), and upgrade part of the original GSM system to meet the exchange and transmission of packet data service. Compared with the original GSM network, some of the new or upgraded equipment is as follows.
Serving GSN (SGSN)
The main functions of SGSN are to perform authentication, mobility management and route selection for the MS, to establish the transmission channel from the MS to the GGSN, receive the MS packet data from the BSS and then transmit it to the GGSN or reverse work through the GPRS backbone network, and conduct billing and service statistics.
Gateway GPRS Supporting Node (GGSN)
Mainly acting as a gateway, GGSN connects with a variety of different external data networks, such as ISDN, PSPDN and LAN. To the external network, GGSN is a router, hence it is also called a GPRS router. The GGSN receives packet data sent by the MS and performs protocol translation to transmit these packet data to a remote TCP/IP or X.25 network or vice versa. In addition, the GGSN also has functions such as address allocation and accounting.
Packet Control Unit (PCU)
PCU is usually located in the BSC and is used for processing data services. It separates packet data services from the GSM voice services at the BSC and transmitted it between the BTS and the SGSN. PCU adds the packet function, controls wireless links, and allows multiple users to occupy the same wireless resource.
Upgrade the Original GSM Network Equipment
GPRS network uses the original GSM base station, which, however, needs to be updated with software; GPRS should add a new mobility management program to achieve GPRS backbone network interconnection through the router; the GSM network system should update software and add new MAP signaling and GPRS signaling.
GPRS Terminal
A new GPRS terminal must be adopted. Three types of GPRS mobile stations are as follows.
• Type A: The ability to provide GPRS service and circuit-switched bearer service simultaneously. That is, GSM voice service can be carried out and a GPRS packet can be received at the same time.
• Type B: Listening to the paging information of GPRS and GSM systems at the same time is allowed, which is attached to GPRS and GSM systems at the same time, but only one of the services is supported at one time.
• Type C: Support either GSM network or GPRS network, manually select and replace the network.
• GPRS terminals can also be made into computer PCMCIA cards for mobile Internet access.
4. What is the Coverage of GPRS Network
Wide Coverage
GPRS communications are able to meet the needs of mountainous areas, cities, and inter-regional access. Although the number of weather stations is large and distributed all over the country, and some of them are located in remote areas and geographically dispersed, the GPRS network has covered all over the country, and the 2G/4G networks can be chosen at will to meet the requirements of weather stations for coverage.
5. What are Differences between GPRS and GPS

Different Definitions
GPS, namely Global Positioning System. In addition to providing real-time, global navigation assistance in the air, sea and land, the invention of GPS can also be used for military services such as intelligence gathering, monitoring and detecting nuclear explosions, and emergency communications
GPRS, namely General Packet Radio Service, is a continuation of GSM. It’s a kind of service that can be chosen by the mobile phone users of GSM.
Different Application Scenarios
GPRS is applied to mobile offices, mobile businesses, mobile information services, mobile Internet, multimedia service, etc.
GPS is applied to road engineering, patrol, car navigation and traffic management of navigation, positioning, measurement, etc.
Different technical features
GPRS has the characteristics of high-speed data transmission, always online, and billing only by data flow, and at the same time, the data is sent and received in groups, billed by flow with the transmission speed at 56~115Kbps.
6. GPRS Technology in 5G

GPRS Network
• GPRS network is the wireless data transmission network provided by China Mobile Company. As long as there are GPRS signals, it can support data wireless transmission. GPRS network has the advantages of wide area coverage, always online, billing by volume, high-speed transmission and so on.
• Wide area coverage: GPRS has good coverage in more than 240 cities in 31 provinces across the country, and it is basically possible to access the internet via GPRS wireless network in any place where mobile phones can make calls.
• Online all the time: The GPRS application will remain online all the time after being activated, which is similar to a wireless dedicated network service.
• Charging by volume: Although GPRS service is always online, you don’t have to worry about the cost, and this is because billing is only performed when communication traffic is generated.
• High-speed transmission: Nowadays, 53.6Kbps peak transmission rate is supported in GPRS, and the theoretical peak transmission is able to reach over100 Kbps.
5G Network
As the latest mobile communication network technology, 5G’s transmission speed is expected to reach tens of GB/s, the whole high-quality film can be downloaded within 1s in 5G network communication. At present, 5G network has successfully reached the transmission speed of 1Gbps in the 28GHz band, while 4G transmission rate is only 75Mbps, downlink speed is 100Mbps, and uplink speed is 30Mbps, and it only has an asymmetric data transmission capacity of more than 2Mb/s. Samsung Electronics Company has achieved this requirement by using an adaptive array transmission method with 64 antenna elements, which means that in 5G networks, smart terminals can be used to share 3D movies and games and enjoy ultra-high picture quality, and this is almost impossible for 4G network communication technology to achieve.
Advantages of 5G Network:
• Fast communication speed: the transmission rate of the communication system can reach 300Mbps, or even up to 1000Mbps.
• Wide network spectrum: the communication bandwidth is much higher than that of cellular system of 3G network, equivalent to 20 times of the W-CDMA 3G network.
• Flexible communication: materials, pictures and videos being downloaded and transmitted in both directions is allowed.
• 5G network also has the characteristics of high intelligence, good compatibility and so on.
GPRS technology and 5G network remote wireless data transmission technology are widely applied in the monitoring of heating supply pipe networks, water supply pipe networks, aquaculture environments, livestock breeding environments, storage tank and warehouses, laboratory collection room environments, atmospheric environments and manufacturing intelligent monitoring. Besides, they are also used in early warning systems.
7. Who Invented GPRS

From the first generation of analog communication systems to the second generation of digital communication systems, and later to 3G, 4G and 5G, mobile communication technology is now developing at a rapid pace. Compared with other mobile communication technologies in the second generation, GSM is the most widely applied. Nevertheless, the GSM system may just exchange data with a transmission rate being 9.6 kbit/s, making it difficult to meet the demand for data services. Therefore, the ETSI introduced GPRS technology.
8. Advantages and Disadvantages of GPRS

Communication Advantages of GPRS
- Wide coverage: GPRS communication is able to meet the needs of mountainous areas, cities, and inter-regional access. Although there are many weather stations distributed all over the country, and some of them are located in remote areas and geographically scattered, GPRS network has covered all over the country, and 2G/4G two kinds of networks can be chosen at will to meet the requirements of weather stations for coverage.
- High data transmission rate: Each weather station transmits data within 10Kbps each time. And currently, the transmission rate of GPRS is around 40Kbps.
- Low communication cost: Specific lines must be equipped to transmit information in a wired way, which is relatively expensive. On the contrary, the use of the GPRS wireless communication method only costs 30 yuan per month minimum, because a 2G communication network is applied in this mode, and it charges according to the data flow. Besides, the resource utilization rate is high in this mode.
- Support for IP and X.25 protocols: Because the GSM network has a wider coverage, GPRS is able to present wireless access to the Internet.
Advantages and Disadvantages of GPRS Communication
In general, GPRS communication technology is characterized by a fast transmission rate, long transmission distance and simple networking, but it is limited by the coverage of base stations, and the signal is weak in poor communication conditions and there are communication dead angles.
Since the GSM network has a wide signal coverage, there is actually a wide geographical area where GPRS services can be used, which is the main advantage of GPRS technology. Secondly, GPRS terminals can roam freely within the signal coverage area, so developers do not need to develop any other communication devices which are the responsibility of operators and are easy to use for users. Finally, due to the popularity of mobile communication terminals, their cost has been greatly reduced, so the hardware cost of using GPRS communication technology in IoT has a greater advantage compared with Wi-Fi or ZigBee.
GPRS terminals need to use the infrastructure of telecom operators when communicating, so a certain fee is required, i.e. data traffic fee, and this service fee limits a large number of devices to connect to the network. In addition, the lower rate of GPRS is another issue. GPRS communication quality is greatly affected by signal strength, and poor communication in places with no signal coverage or weakness may affect service completion.
9. Application Instances of GPRS

The Environment of Field Terminal and Dispersed Transmission Distance
A pretty important benefit of wireless network communication is that specialized wireless communication networks (such as digital radio stations, WiMax, WLAN, etc.) cannot be realized.
Industry Site Environment
If there is now a need to operate data on the move as well as to collect information about the site equipment, collect information about the site in the field, etc., and a wired communication environment cannot be provided, the use of GPRS wireless network may be a good choice. The target rate of the GPRS network is now high as most regions of the country has GPRS signal targets.
Appropriate Real-Time Data Requirements
Currently, the data transmission latency on GPRS networks is within a few seconds. Under most situations, the average total latency for GPRS data communication is around 2 seconds. In other words, a data packet sent from the GPRS DTU will reach the data center in about 2 seconds. On the contrary, the packet from the data will arrive at the GPRS DTU as well after about 2 seconds.
Generally speaking, the real-time performance of GPRS is able to meet the needs of many applications in the industry field. However, in some specific applications, the GPRS communication method may not be appropriate if an average delay of about 2 seconds is not tolerated.
From another perspective, if a system designed by us will transmit data over a GPRS network, then we need to take this delay into account when we design the communication protocol.
Appropriate Data Communication Rate
The data communication speed between the GPRS DTU and the data center is usually from 10kbps to 60kbps, which means that the GPRS DTU may continue to send data to the center at the speed of 10bps-60kbps, or vice versa. (Note: The average data communication rate of a home CDMA network is about 40kbps-90kbps).
10. Development History of GPRS
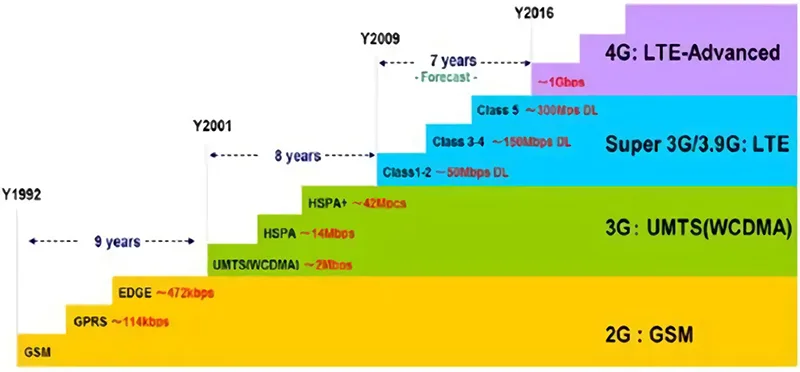
Mobile communication technology has developed from the first generation of analog communication systems to the second generation of digital communication systems, and then 3G, 4G and 5G are developing at a rapid pace. Compared with other mobile communication technologies in the second generation, GSM is the most widely applied. But the GSM system is just able to exchange data in the circuit domain with its highest transmission rate being 9.6kbit/s, which is hard to reach the requirement of data services, and for this reason, the ETSI issued GPRS.
In order to realize the support from the previous voice service to the new data service, GPRS overlaps with the original GSM network to support the high-speed packet data network and provides users with WAP browsing (Internet page), E-mail and other functions.















